Vibrational Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy using an FVS-6000 Spectrometer
January 4, 2024
Introduction
Overview of Vibrational Circular Dichroism
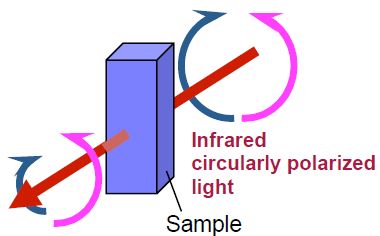
Vibrational Circular Dichroism (VCD) is a spectroscopic method to measure the difference in absorbance intensity between left-and right-hand circularly polarized light as shown in Figure 1. The advantage of vibrational circular dichroism is that it can be applied to almost all organic compounds in the same way as infrared (IR) spectroscopy. In addition, the absolute configuration of a sample can be determined by comparing the measured with results from ab-initio molecular orbital calculations, . However, since the peak intensity of VCD spectra are 1,000 to 10,000 times weaker than that of standard IR spectra, spectroscopic instruments with high sensitivity and stability, with very small baseline fluctuations are required. The FVS-6000 VCD spectrometer includes the highest sensitivity narrow band MCT detectors, coupled with optical filter technology and a thermostatted Photo Elastic Modulator (PEM) to accurately measure the very weak VCD peaks. The results of several typical chiral compounds and hemoglobin as a model protein using the FVS-6000 are reported here.
It is generally understood that chiral compounds have different bioactivities depending upon the absolute configuration of each compound. Some familiar examples include glutamic acid and thalidomide. L-glutamic acid demonstrates the “Umami” taste*1, while D-glutamic acid has a bitter taste, similarly, the R- form of thalidomide is a sedative, but the S- form has teratogenic activity. Thus, the separation and study of chiral compounds is critical for many reasons.
The functionalities of chiral compounds have been studied for the development of advanced molecules for many different applications. These studies have spread to new fields such as natural products, pharmaceuticals and other functional molecules. The structural analysis of chiral compounds is a very important topic, with X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) using UV-visible light being employed as primary methods for structural analysis. In this paper, the further analysis of chiral compounds using Vibrational Circular Dichroism (VCD) using infrared light will be presented.
*1 Umami is considered to be the fifth taste sensation in addition to sweet, acid, salty and bitter tastes.

Keywords
260-PO-0224, Vibrational Circular Dichroism, VCD, alpha pinene, absolute stereochemistry, IR spectroscopy, protein secondary structure, alpha helix, beta sheet, ab-initio structural calculation
Results
Measurement results
Figures 3 through 6 illustrate the measurement results for alpha-pinene; 1,1-Bi-2-naphthol; proline and hemoglobin, respectively. Both IR and VCD spectra can be obtained by the FVS-6000. The analysis of molecular structure and absolute configuration of chiral compounds can be determined from both the IR and the VCD spectra.
Figure 3 demonstrates the IR and VCD spectra of alpha-pinene which is a typical standard molecule used to validate a VCD instrument. IR spectra of the R- and S- forms of alpha-pinene are completely overlapped, while their VCD spectra are symmetric, clearly identifying each alpha-pinene enantiomer. Since the measured VCD spectra correlate accurately with typical alpha-pinene spectra, it is confirmed that high quality VCD spectra can be obtained using the FVS-6000.
Figure 4 outlines measurement results for 1,1-Bi-2-naphthol which is used as a ligand for transition-metal catalyzed asymmetric synthesis and is a precursor for chiral ligands such as BINAP. The small peaks due to the anisotropy factor g value (VCD peak/IR peak) around 1600 and 1500 cm-1 attributed to the benzene ring are clearly shown. These results demonstrate that the FVS-6000 is a very effective system for evaluation of chiral compounds which have similar structures.
Figure 5 illustrates the measurement results of the amino acid proline. Good, symmetrical VCD spectra were obtained for both the D- and L- forms. Since amino acids demonstrate different bioactivities between the D- and L- forms, studies regarding structure and bioactivity are increasingly popular. Liquid samples can be easily measured by VCD so the structural analysis of amino acids can be performed in typical physiological conditions.
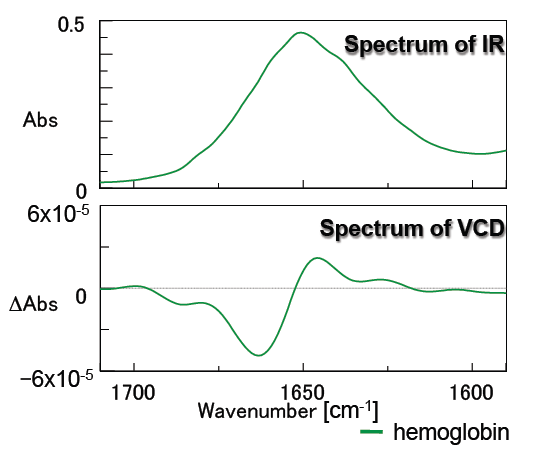
Figure 6 contains the measurement results for hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a spherical protein rich in alpha-helix structures, its VCD spectrum is very different from that of concanavalin A, which is rich in beta-sheet structures.
The correlation of VCD spectral results with information obtained from ECD and IR can provide much more accurate secondary structure analysis of proteins in solvents. We also believe that VCD can also be a powerful tool for the analysis of other chiral macro molecules such as DNA and chiral polymers.
In this paper, the standard performance and measurement results of typical chiral compounds using the FVS-6000 were reported and we believe the FVS-6000 can be an essential and indispensable tool for analysis of chiral compounds.
Measurement condition
| Model name: | FVS-6000 |
| Resolution: | 4 cm-1 |
| Detector: | MCT-V |
| Accumulation: | 1000 (alpha-pinene and 1,1?-Bi-2-naphthol), 2500 (proline), 2000 (hemoglobin) |
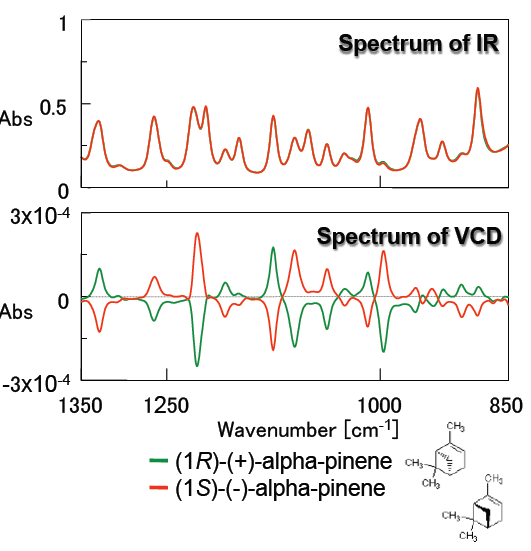
(neat, 50 um pathlength BaF2 liquid cell)
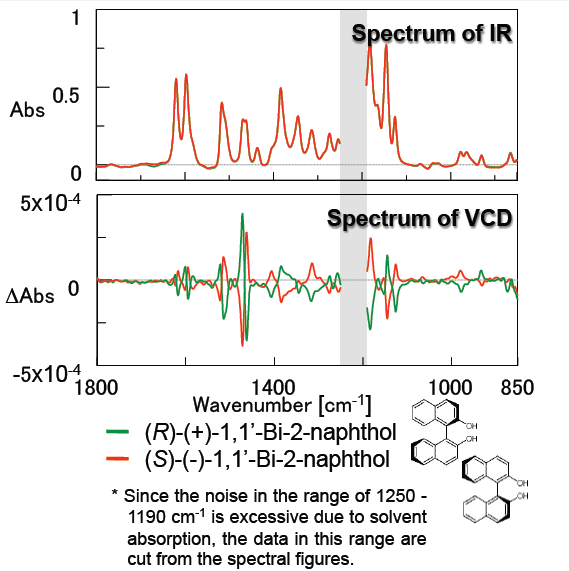
(solvent: CHCl3, concentration: 0.162 M, 50 um pathlength BaF2 liquid cell)
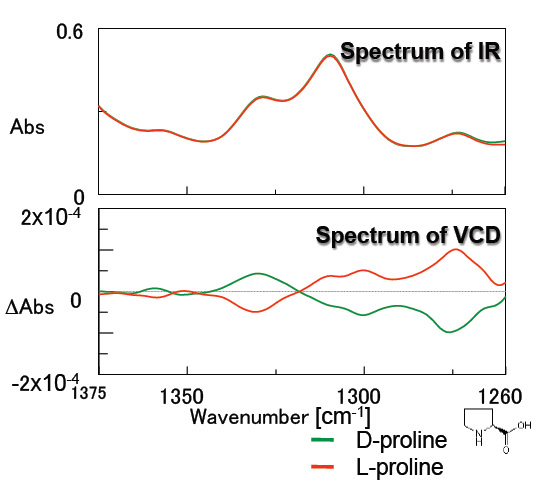
(solvent: D2O, concentration: 0.9 M, 25 um pathlength CaF2 liquid cell)
(solvent: D2O, concentration: 50 mg/mL,
25 um pathlength CaF2 liquid cell)
Featured Products:

Vibrational Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy using an FVS-6000 Spectrometer
Introduction
Overview of Vibrational Circular Dichroism
Vibrational Circular Dichroism (VCD) is a spectroscopic method to measure the difference in absorbance intensity between left-and right-hand circularly polarized light as shown in Figure 1. The advantage of vibrational circular dichroism is that it can be applied to almost all organic compounds in the same way as infrared (IR) spectroscopy. In addition, the absolute configuration of a sample can be determined by comparing the measured with results from ab-initio molecular orbital calculations, . However, since the peak intensity of VCD spectra are 1,000 to 10,000 times weaker than that of standard IR spectra, spectroscopic instruments with high sensitivity and stability, with very small baseline fluctuations are required. The FVS-6000 VCD spectrometer includes the highest sensitivity narrow band MCT detectors, coupled with optical filter technology and a thermostatted Photo Elastic Modulator (PEM) to accurately measure the very weak VCD peaks. The results of several typical chiral compounds and hemoglobin as a model protein using the FVS-6000 are reported here.
It is generally understood that chiral compounds have different bioactivities depending upon the absolute configuration of each compound. Some familiar examples include glutamic acid and thalidomide. L-glutamic acid demonstrates the “Umami” taste*1, while D-glutamic acid has a bitter taste, similarly, the R- form of thalidomide is a sedative, but the S- form has teratogenic activity. Thus, the separation and study of chiral compounds is critical for many reasons.
The functionalities of chiral compounds have been studied for the development of advanced molecules for many different applications. These studies have spread to new fields such as natural products, pharmaceuticals and other functional molecules. The structural analysis of chiral compounds is a very important topic, with X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) using UV-visible light being employed as primary methods for structural analysis. In this paper, the further analysis of chiral compounds using Vibrational Circular Dichroism (VCD) using infrared light will be presented.
*1 Umami is considered to be the fifth taste sensation in addition to sweet, acid, salty and bitter tastes.


Keywords
260-PO-0224, Vibrational Circular Dichroism, VCD, alpha pinene, absolute stereochemistry, IR spectroscopy, protein secondary structure, alpha helix, beta sheet, ab-initio structural calculation
Results
Measurement results
Figures 3 through 6 illustrate the measurement results for alpha-pinene; 1,1-Bi-2-naphthol; proline and hemoglobin, respectively. Both IR and VCD spectra can be obtained by the FVS-6000. The analysis of molecular structure and absolute configuration of chiral compounds can be determined from both the IR and the VCD spectra.
Figure 3 demonstrates the IR and VCD spectra of alpha-pinene which is a typical standard molecule used to validate a VCD instrument. IR spectra of the R- and S- forms of alpha-pinene are completely overlapped, while their VCD spectra are symmetric, clearly identifying each alpha-pinene enantiomer. Since the measured VCD spectra correlate accurately with typical alpha-pinene spectra, it is confirmed that high quality VCD spectra can be obtained using the FVS-6000.
Figure 4 outlines measurement results for 1,1-Bi-2-naphthol which is used as a ligand for transition-metal catalyzed asymmetric synthesis and is a precursor for chiral ligands such as BINAP. The small peaks due to the anisotropy factor g value (VCD peak/IR peak) around 1600 and 1500 cm-1 attributed to the benzene ring are clearly shown. These results demonstrate that the FVS-6000 is a very effective system for evaluation of chiral compounds which have similar structures.
Figure 5 illustrates the measurement results of the amino acid proline. Good, symmetrical VCD spectra were obtained for both the D- and L- forms. Since amino acids demonstrate different bioactivities between the D- and L- forms, studies regarding structure and bioactivity are increasingly popular. Liquid samples can be easily measured by VCD so the structural analysis of amino acids can be performed in typical physiological conditions.
Figure 6 contains the measurement results for hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a spherical protein rich in alpha-helix structures, its VCD spectrum is very different from that of concanavalin A, which is rich in beta-sheet structures.
The correlation of VCD spectral results with information obtained from ECD and IR can provide much more accurate secondary structure analysis of proteins in solvents. We also believe that VCD can also be a powerful tool for the analysis of other chiral macro molecules such as DNA and chiral polymers.
In this paper, the standard performance and measurement results of typical chiral compounds using the FVS-6000 were reported and we believe the FVS-6000 can be an essential and indispensable tool for analysis of chiral compounds.
Measurement condition
| Model name: | FVS-6000 |
| Resolution: | 4 cm-1 |
| Detector: | MCT-V |
| Accumulation: | 1000 (alpha-pinene and 1,1?-Bi-2-naphthol), 2500 (proline), 2000 (hemoglobin) |

(neat, 50 um pathlength BaF2 liquid cell)

(solvent: CHCl3, concentration: 0.162 M, 50 um pathlength BaF2 liquid cell)

(solvent: D2O, concentration: 0.9 M, 25 um pathlength CaF2 liquid cell)

(solvent: D2O, concentration: 50 mg/mL,
25 um pathlength CaF2 liquid cell)

 Download This Application
Download This Application