Measurement of Microparticles in Facial Cleansers using IR Microscopy with Clear-View™ ATR
March 13, 2024Introduction
IR Microscopes have been widely used for the identification and imaging of microscopic samples to visualize the chemical composition and distribution. Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) methods require little to no sample preparation or pre-treatment and allow precise measurement of particles at the micron level, which can be difficult by transmission or reflection. Typically, ATR objectives are not suitable for samples that move or are damaged when placed in contact with the crystal since the area of interest must be in the center of the crystal. In addition, direct observation of the sample through the ATR crystal is normally impossible, making it difficult to confirm the exact point. The IRT-5200/7200 microscopes include IQ Mapping, which provides accurate measurement even if the sample area of interest is not located in the center of the crystal. Furthermore, Clear-View™ ATR objectives (series of ATR-5000-S) have been developed for observation of the sample before and during crystal contact with the sample.
Experimental

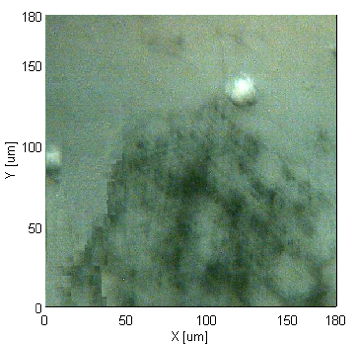
This application describes the measurement of a black particle found in the paste filler of a facial cleanser (red square in Fig. 1) using an IRT-5200 microscope with Clear-View™ ATR objective (ATR-5000-SS) and IQ Mapping. By combining IQ Mapping with a ClearView™ ATR objective, an optical image in contact with the sample and spectra from not only the center of the crystal, but the entire field of view can be obtained without any contamination or cumbersome repeated contact to the sample with the crystal. An optical image of the facial cleanser was taken when the Clear-View™ ATR was in contact with the black particle (Fig. 2), guaranteeing the recorded image accurately matches the measured positions to generate a chemical image.
| Measurement Conditions | |||
| Instrument | FT/IR-6100 + IRT-5200 | Objective | ATR-5000-SS (ZnS Crystal) |
| Detector | Narrow-band MCT | Measurement Spot | 37 x 37 µm (IQ Mapping) |
| Resolution | 8 cm-1 | Aperture Size | 5 x 5 µm |
| Accumulation | 16 times | Measurement Area | 180 x 180 µm |
Keywords
130-AT-0229
Results
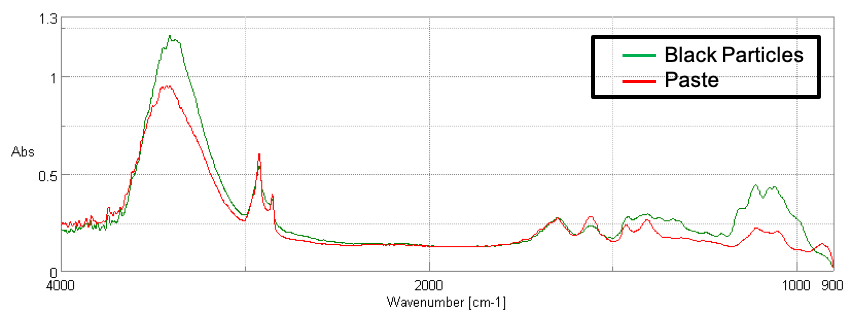
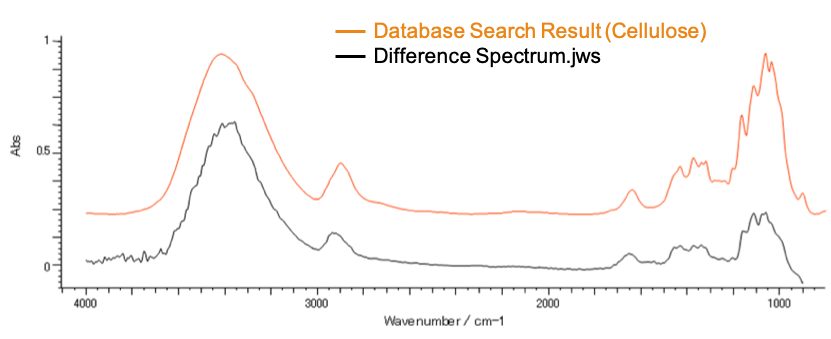
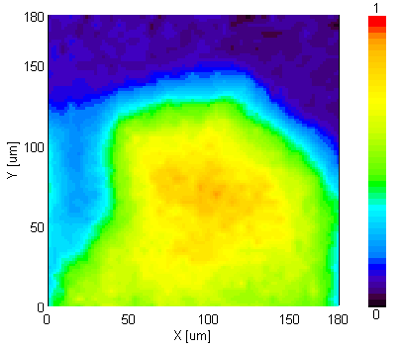
The measured spectra of the paste and black particles, which were ATR corrected for abnormal dispersion, are shown in Figure 3. The main component in both spectra was identified as Glycerin; however, the black particle appears to have an additional component. Spectral subtraction was performed, and the resulting difference spectrum identified cellulose as the additional component in the black particle (Fig. 4). A chemical image was created based on the peak height of the glycoside bond of cellulose at 1,056 cm-1 (Fig. 5). The results confirm that cellulose is evenly distributed throughout the black particles, which are scattered throughout the facial cleanser. Based on the identification of the paste and black particles, it is assumed the paste washes dirt away and keeps the skin moisturized, while the black particles adsorb the surplus sebum and perspiration.

Measurement of Microparticles in Facial Cleansers using IR Microscopy with Clear-View™ ATR
Introduction
IR Microscopes have been widely used for the identification and imaging of microscopic samples to visualize the chemical composition and distribution. Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) methods require little to no sample preparation or pre-treatment and allow precise measurement of particles at the micron level, which can be difficult by transmission or reflection. Typically, ATR objectives are not suitable for samples that move or are damaged when placed in contact with the crystal since the area of interest must be in the center of the crystal. In addition, direct observation of the sample through the ATR crystal is normally impossible, making it difficult to confirm the exact point. The IRT-5200/7200 microscopes include IQ Mapping, which provides accurate measurement even if the sample area of interest is not located in the center of the crystal. Furthermore, Clear-View™ ATR objectives (series of ATR-5000-S) have been developed for observation of the sample before and during crystal contact with the sample.
Experimental

This application describes the measurement of a black particle found in the paste filler of a facial cleanser (red square in Fig. 1) using an IRT-5200 microscope with Clear-View™ ATR objective (ATR-5000-SS) and IQ Mapping. By combining IQ Mapping with a ClearView™ ATR objective, an optical image in contact with the sample and spectra from not only the center of the crystal, but the entire field of view can be obtained without any contamination or cumbersome repeated contact to the sample with the crystal. An optical image of the facial cleanser was taken when the Clear-View™ ATR was in contact with the black particle (Fig. 2), guaranteeing the recorded image accurately matches the measured positions to generate a chemical image.

| Measurement Conditions | |||
| Instrument | FT/IR-6100 + IRT-5200 | Objective | ATR-5000-SS (ZnS Crystal) |
| Detector | Narrow-band MCT | Measurement Spot | 37 x 37 µm (IQ Mapping) |
| Resolution | 8 cm-1 | Aperture Size | 5 x 5 µm |
| Accumulation | 16 times | Measurement Area | 180 x 180 µm |
Results

The measured spectra of the paste and black particles, which were ATR corrected for abnormal dispersion, are shown in Figure 3. The main component in both spectra was identified as Glycerin; however, the black particle appears to have an additional component. Spectral subtraction was performed, and the resulting difference spectrum identified cellulose as the additional component in the black particle (Fig. 4). A chemical image was created based on the peak height of the glycoside bond of cellulose at 1,056 cm-1 (Fig. 5). The results confirm that cellulose is evenly distributed throughout the black particles, which are scattered throughout the facial cleanser. Based on the identification of the paste and black particles, it is assumed the paste washes dirt away and keeps the skin moisturized, while the black particles adsorb the surplus sebum and perspiration.


Keywords
130-AT-0229

 Download This Application
Download This Application