Monitoring of Degree of Crosslinking for Epoxy Resins using Raman Spectroscopy
April 16, 2025Introduction
Epoxy resins are used in a wide range of fields, such as adhesives, coatings, and electronic components; it is important to monitor the curing degree of epoxy materials for manufacturing and quality control process. The ISO 20368 specified method for evaluating the degree of curing involves tracking the decrease in epoxy groups consumed during the curing process using a Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometer. However, sample preparation is time consuming and requires the sample to be sandwiched between silicon wafers. To avoid these issues, we attempted to use a Raman spectrometer to monitor the curing process. A Raman spectrum can be obtained simply by placing a sample on a stage and irradiating it with a laser beam.
This report describes monitoring results for the curing process for epoxy adhesives using the JASCO Palmtop Raman spectrometer, which can easily perform measurements on bulk samples.
Experimental
Epoxy adhesives for which the degree of curing was previously determined using FT-IR spectroscopy based on ISO 20368, as reported in a previous application note, were evaluated using a JASCO palmtop Raman spectrometer, and the results were compared. The measurements were conducted by spreading the mixed epoxy resin on aluminum foil and placing it on the stage of a dedicated sample chamber (Figure 1). This sample chamber allows measurements to be performed in a light-shielded environment.
Samples
Two-component mixed epoxy resins, three different adhesives
Table 1 Curing characteristics of adhesives at around 20ºC
System

Instrument: PR-1w Palmtop Raman spectrometer
Accessory: PR-1-DS Sample chamber
Software: PR-ITS-1W Interval measurement analysis program
Parameters
Laser wavelength: 785 nm
Laser power: 50 mW (high)
Exposure time: 4 sec
Accumulations: 4
Time interval: 5 min
Data points: 289 (24 hours)
Temperature: 23ºC to 25ºC
Humidity: 40ºC to 45%

Upper: Changes in number of epoxy groups (Raman), Lower: Changes in degree of curing (IR)
* The values on the y-axis of the upper panels are inverted to facilitate comparison with the results in the lower panels.
Keywords
Epoxy resin, adhesive, degree of curing, monitoring, time variation, reaction tracking, interval measurement, palmtop Raman spectrometer
Results
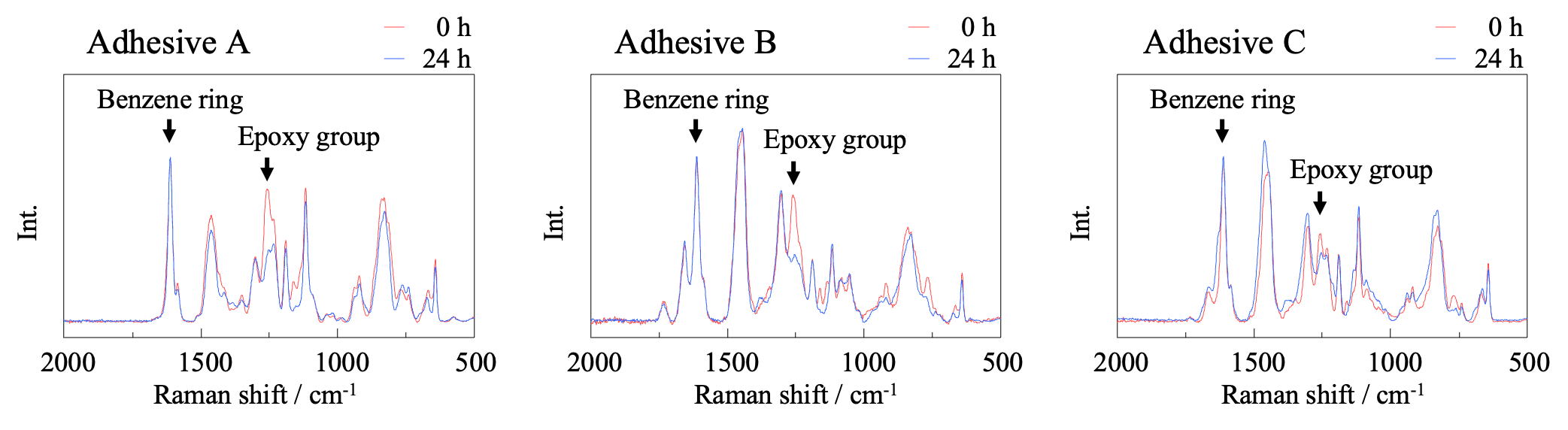
The ratio of the height of the peak at 1250 cm-1, assigned to epoxy groups, to the height of the peak at 1600 cm-1, assigned to the benzene ring (which does not change during curing), is calculated from the Raman spectrum (Figure 2).
The decrease in the number of epoxy groups due to curing of the adhesive (Figure 3, upper panels) is similar to the change in the degree of curing determined using IR spectroscopy (Figure 3, lower panels). This indicates that the degree of curing can be successfully monitored using the JASCO palmtop Raman spectrometer. As can be seen, even for continuous measurements for 24 hours, the reaction process could be monitored stably without any drift or other effects.
Conclusion
As an alternative to IR spectroscopy for evaluating the degree of curing in accordance with ISO 20368, the JASCO Palmtop Raman spectrometer allows stable long-term monitoring of the curing process without the need for complicated sample preparation. As shown by its ability to accurately distinguish the reaction progress for three different epoxy resins, this method can be applied to monitor a wide range of processes.
Related Application Note: 100-TR-0285 Evaluation of Degree of Crosslinking for Epoxy Resins based on ISO 20368
References
Applicative Solution Lab Division E. Taira

Monitoring of Degree of Crosslinking for Epoxy Resins using Raman Spectroscopy
Introduction
Epoxy resins are used in a wide range of fields, such as adhesives, coatings, and electronic components; it is important to monitor the curing degree of epoxy materials for manufacturing and quality control process. The ISO 20368 specified method for evaluating the degree of curing involves tracking the decrease in epoxy groups consumed during the curing process using a Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometer. However, sample preparation is time consuming and requires the sample to be sandwiched between silicon wafers. To avoid these issues, we attempted to use a Raman spectrometer to monitor the curing process. A Raman spectrum can be obtained simply by placing a sample on a stage and irradiating it with a laser beam.
This report describes monitoring results for the curing process for epoxy adhesives using the JASCO Palmtop Raman spectrometer, which can easily perform measurements on bulk samples.
Experimental
Epoxy adhesives for which the degree of curing was previously determined using FT-IR spectroscopy based on ISO 20368, as reported in a previous application note, were evaluated using a JASCO palmtop Raman spectrometer, and the results were compared. The measurements were conducted by spreading the mixed epoxy resin on aluminum foil and placing it on the stage of a dedicated sample chamber (Figure 1). This sample chamber allows measurements to be performed in a light-shielded environment.
Samples
Two-component mixed epoxy resins, three different adhesives
Table 1 Curing characteristics of adhesives at around 20ºC
System

Instrument: PR-1w Palmtop Raman spectrometer
Accessory: PR-1-DS Sample chamber
Software: PR-ITS-1W Interval measurement analysis program
Parameters
Laser wavelength: 785 nm
Laser power: 50 mW (high)
Exposure time: 4 sec
Accumulations: 4
Time interval: 5 min
Data points: 289 (24 hours)
Temperature: 23ºC to 25ºC
Humidity: 40ºC to 45%


Upper: Changes in number of epoxy groups (Raman), Lower: Changes in degree of curing (IR)
* The values on the y-axis of the upper panels are inverted to facilitate comparison with the results in the lower panels.
Results
The ratio of the height of the peak at 1250 cm-1, assigned to epoxy groups, to the height of the peak at 1600 cm-1, assigned to the benzene ring (which does not change during curing), is calculated from the Raman spectrum (Figure 2).
The decrease in the number of epoxy groups due to curing of the adhesive (Figure 3, upper panels) is similar to the change in the degree of curing determined using IR spectroscopy (Figure 3, lower panels). This indicates that the degree of curing can be successfully monitored using the JASCO palmtop Raman spectrometer. As can be seen, even for continuous measurements for 24 hours, the reaction process could be monitored stably without any drift or other effects.
Conclusion
As an alternative to IR spectroscopy for evaluating the degree of curing in accordance with ISO 20368, the JASCO Palmtop Raman spectrometer allows stable long-term monitoring of the curing process without the need for complicated sample preparation. As shown by its ability to accurately distinguish the reaction progress for three different epoxy resins, this method can be applied to monitor a wide range of processes.
Related Application Note: 100-TR-0285 Evaluation of Degree of Crosslinking for Epoxy Resins based on ISO 20368
Keywords
Epoxy resin, adhesive, degree of curing, monitoring, time variation, reaction tracking, interval measurement, palmtop Raman spectrometer
References
Applicative Solution Lab Division E. Taira

 Download This Application
Download This Application