Evaluation of Anti-Reflection Films using Absolute Reflectance Measurement
January 5, 2024
Introduction

Anti-reflection films are used for a variety of applications and wavelength regions; for windows and lens in the visible region to optical communication devices and materials in the near infrared region. With the demand and variance for these materials, the amount of reflectivity allowable has decreased to less than 0.1% reflectance.
An absolute reflectance measurement accessory can be used to evaluate the reflectance of films by changing the incident angle, detection angle, or polarization of the incident light. In this application note, the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory is used to measure film samples for both the visible and near-infrared regions with less than 0.1% reflectance.
Experimental
The linearity measurements were obtained using 66.7, 133.3, 200.0, and 266.6 mg/L of KMnO4 solution for the visible region and ND filter A and B for the infrared region.
For the visible region, the dark measurement is carried out using the masking shield of the cell holder of the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory. The baseline measurement is obtained using water. For the infrared region, the dark measurement is performed identical to the visible region and the baseline measurement is obtained with air. Three sample measurements are performed with the filters: ND filter A set in the sample holder, with ND filter B not parallel to filter A, and with ND filter B in the sample holder.
| Linearity Measurement Conditions | |||
| Visible | NIR | ||
| Bandwidth | L5.0 nm | Bandwidth | 40.0 nm |
| Response | 3.84 sec | Response | 3.84 sec |
| Scan Speed | 100 nm/min | Scan Speed | 100 nm/min |
| Data Interval | 1 nm | Data Interval | 1 nm |
The reflection measurements of three antireflection films with different coatings were obtained using the following measurements parameters. The dark measurements were carried out with the masking shield in the sample holder. The baseline measurement was obtained with air and the sample measurements were obtained by placing the samples in the sample holder.
| Film Reflectance Measurement Conditions | |||
| Visible | NIR | ||
| Bandwidth | L5.0 nm | Bandwidth | 40 nm (V-770), 10 nm (V-780) |
| Response | 0.96 sec | Response | 3.84 sec |
| Scan Speed | 200 nm/min | Scan Speed | 100 nm/min |
| Incident Angle | 5° | Incident Angle | 5° |
| Data Interval | 0.5 nm | Data Interval | 1 nm |
| Polarization | N-polarized | Polarization | N-polarized |
Keywords
190-UV-0040, V-770/780, UV-Visible/NIR, ARMN-920/920i Automated Absolute Reflectance measurement accessory, Materials, Films
Results
The linearity measurements of KMnO4 in the visible region are shown in Figure 1 and the calibration curve at 526 nm is shown in Figure 2. In the absorbance range from 1 to 4, the R2 value illustrates the highest correlation (more than 0.999), indicating the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory can obtain absorbances up to 4 AU and therefore transmittance and reflectance values can be obtained up to 0.01%.
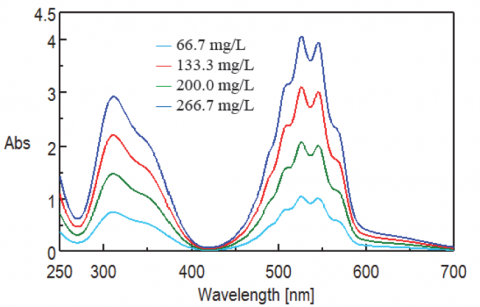
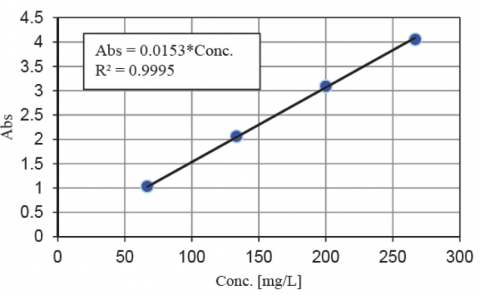
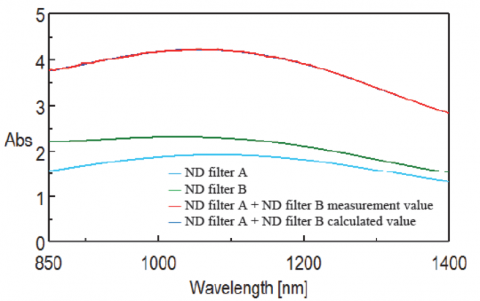
Figure 3 shows the absorption spectrum of the ND filters. The spectrum of the individual ND filter A and B agrees with the sum of the two filters. This also indicates that the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory can obtain absorbances up to 4 AU and therefore transmittance and reflectance values can be obtained up to 0.01%.
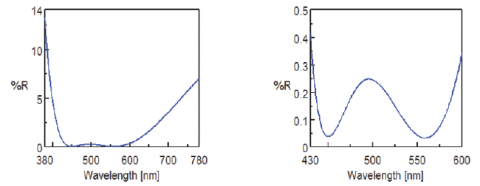
The antireflection films were measured using a V-770 and V-780 and the reflectance data are shown in Figure 4 for the visible region, and the near-infrared spectra are shown in Figures 5 and 6. Table 1 provides the reflectance values of the minima. These figures illustrate that measurements with less than 0.1% reflectance can be obtained in both the visible and near-infrared regions.
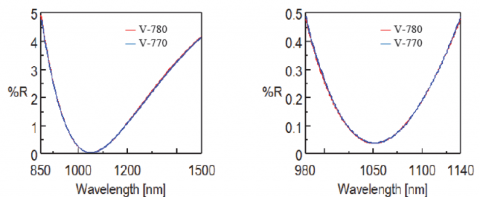
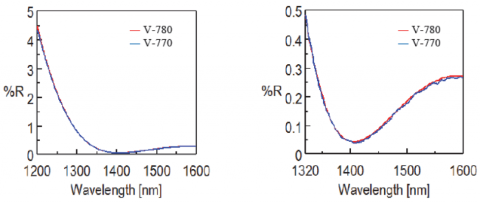
Table 1. Minima reflectance values.
| AR Coat Vis | AR Coat NIR 1 | AR Coat NIR 2 | ||||
| Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | |
| V-770 | 450.5 | 0.03681 | 1049 | 0.03655 | 1406 | 0.03703 |
| V-780 | -- | -- | 1049 | 0.03655 | 1406 | 0.04235 |
Conclusion
The V-770 and V-780 provide nearly identical spectra in regards to the S/N from 980 to 1140 nm. However, from 1320 to 1600 nm the V-780 obtains a higher S/N due to the InGaAs detector. The V-770 is equipped with a PbS detector which has high sensitivity over a wider wavelength range, while the InGaAs detector of the V-780 has a higher sensitivity over a shorter wavelength range. The V-770 is therefore suitable for measurements with a wide wavelength range and the V-780 is ideal for high sensitivity measurements.
Featured Products:
-

Wide range UV-Visible/Near Infrared Spectrophotometer with PbS detector for wavelengths up to 3200nm
V-770 UV-Visible/NIR Spectrophotometer
-

A high resolution UV-Visible double-beam, double-monochromator spectrophotometer with exceptional stray light and absorbance linearity
V-760 UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
-

A high sensitivity UV-Visible/NIR Spectrophotometer with InGaAs detector for wavelengths up to1600nm
V-780 UV-Visible/NIR Spectrophotometer

Evaluation of Anti-Reflection Films using Absolute Reflectance Measurement
Introduction

Anti-reflection films are used for a variety of applications and wavelength regions; for windows and lens in the visible region to optical communication devices and materials in the near infrared region. With the demand and variance for these materials, the amount of reflectivity allowable has decreased to less than 0.1% reflectance.
An absolute reflectance measurement accessory can be used to evaluate the reflectance of films by changing the incident angle, detection angle, or polarization of the incident light. In this application note, the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory is used to measure film samples for both the visible and near-infrared regions with less than 0.1% reflectance.
Experimental
The linearity measurements were obtained using 66.7, 133.3, 200.0, and 266.6 mg/L of KMnO4 solution for the visible region and ND filter A and B for the infrared region.
For the visible region, the dark measurement is carried out using the masking shield of the cell holder of the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory. The baseline measurement is obtained using water. For the infrared region, the dark measurement is performed identical to the visible region and the baseline measurement is obtained with air. Three sample measurements are performed with the filters: ND filter A set in the sample holder, with ND filter B not parallel to filter A, and with ND filter B in the sample holder.
| Linearity Measurement Conditions | |||
| Visible | NIR | ||
| Bandwidth | L5.0 nm | Bandwidth | 40.0 nm |
| Response | 3.84 sec | Response | 3.84 sec |
| Scan Speed | 100 nm/min | Scan Speed | 100 nm/min |
| Data Interval | 1 nm | Data Interval | 1 nm |
The reflection measurements of three antireflection films with different coatings were obtained using the following measurements parameters. The dark measurements were carried out with the masking shield in the sample holder. The baseline measurement was obtained with air and the sample measurements were obtained by placing the samples in the sample holder.
| Film Reflectance Measurement Conditions | |||
| Visible | NIR | ||
| Bandwidth | L5.0 nm | Bandwidth | 40 nm (V-770), 10 nm (V-780) |
| Response | 0.96 sec | Response | 3.84 sec |
| Scan Speed | 200 nm/min | Scan Speed | 100 nm/min |
| Incident Angle | 5° | Incident Angle | 5° |
| Data Interval | 0.5 nm | Data Interval | 1 nm |
| Polarization | N-polarized | Polarization | N-polarized |
Results
The linearity measurements of KMnO4 in the visible region are shown in Figure 1 and the calibration curve at 526 nm is shown in Figure 2. In the absorbance range from 1 to 4, the R2 value illustrates the highest correlation (more than 0.999), indicating the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory can obtain absorbances up to 4 AU and therefore transmittance and reflectance values can be obtained up to 0.01%.



Figure 3 shows the absorption spectrum of the ND filters. The spectrum of the individual ND filter A and B agrees with the sum of the two filters. This also indicates that the automated absolute reflectance measurement accessory can obtain absorbances up to 4 AU and therefore transmittance and reflectance values can be obtained up to 0.01%.

The antireflection films were measured using a V-770 and V-780 and the reflectance data are shown in Figure 4 for the visible region, and the near-infrared spectra are shown in Figures 5 and 6. Table 1 provides the reflectance values of the minima. These figures illustrate that measurements with less than 0.1% reflectance can be obtained in both the visible and near-infrared regions.


Table 1. Minima reflectance values.
| AR Coat Vis | AR Coat NIR 1 | AR Coat NIR 2 | ||||
| Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | Wavelength (nm) | Reflectance (%) | |
| V-770 | 450.5 | 0.03681 | 1049 | 0.03655 | 1406 | 0.03703 |
| V-780 | -- | -- | 1049 | 0.03655 | 1406 | 0.04235 |
Conclusion
The V-770 and V-780 provide nearly identical spectra in regards to the S/N from 980 to 1140 nm. However, from 1320 to 1600 nm the V-780 obtains a higher S/N due to the InGaAs detector. The V-770 is equipped with a PbS detector which has high sensitivity over a wider wavelength range, while the InGaAs detector of the V-780 has a higher sensitivity over a shorter wavelength range. The V-770 is therefore suitable for measurements with a wide wavelength range and the V-780 is ideal for high sensitivity measurements.
Keywords
190-UV-0040, V-770/780, UV-Visible/NIR, ARMN-920/920i Automated Absolute Reflectance measurement accessory, Materials, Films

 Download This Application
Download This Application