Decomposition of Carbon Tetrachloride (CCI4) with Supercritical Water
January 5, 2024
Introduction
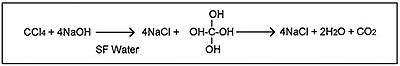
Carbon tetrachloride can be decomposed to sodium chloride, water and carbon dioxide in supercritical water containing sodium hydroxide following the reaction path shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 2 shows the flow diagram of this reaction system. Carbon tetrachloride and sodium hydroxide aqueous solutions are pumped respectively into reaction coil for decomposition, and then the reaction product is collected in a glass tube placed downstream of the back-pressure regulator (5) as shown in Fig. 2. Decomposition efficiency at each reaction temperature was calculated by measuring the amount of sodium chloride (chloride ion) by ion-chromatography (see Fig. 3) and the amount of remaining carbon tetrachloride by gas chromatography (see Fig. 4), respectively.
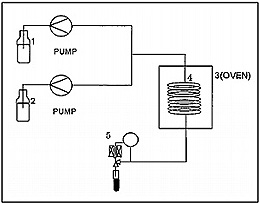
Conditions: Reagent 1: 5 M NaOH 2.0 mL/min; Sample reagent 2: CCI4 0.1 mL/min; Reaction temperature: 380, 350, 300, 250, 200, 40°C; Reaction coil 4: Hastelloy-C276 tube (0.5 mm I.D. x 5 m Length) = 981 µL; Back pressure: 30 MPa.
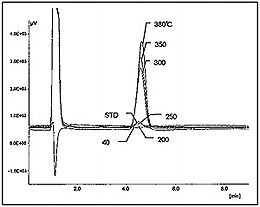
Conditions: Detector: Shodex CD-5; Column: Shodex IC I-524A; Shodex IC I-524AP; Eluent: 1.5 mM Phthalic acid adjusted; pH 3.0 with Tris.; Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min; Column temperature: 40°C; Injection volume: 5 µL; Sample: STD; NaCl 1.3 ppm; UNK; x 500.
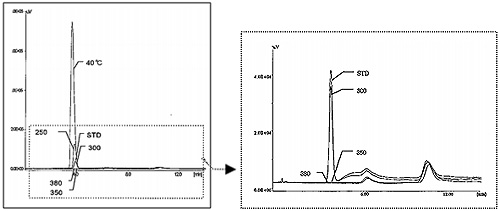
Conditions: GC: GC-5890 (HP); Detector: FID 103; Column: Cemipak NOT Sus Col.6ft x 2 mm I.D.; Mobile phase: N2 at 3 kPa; Column temperature: 60°C; Injection volume: 5 µL; Sample: 5 mL/mL each of effluent at 380, 350, 300 and 40°C.
Keywords
820002S
Featured Products:

Decomposition of Carbon Tetrachloride (CCI4) with Supercritical Water
Introduction
Carbon tetrachloride can be decomposed to sodium chloride, water and carbon dioxide in supercritical water containing sodium hydroxide following the reaction path shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 2 shows the flow diagram of this reaction system. Carbon tetrachloride and sodium hydroxide aqueous solutions are pumped respectively into reaction coil for decomposition, and then the reaction product is collected in a glass tube placed downstream of the back-pressure regulator (5) as shown in Fig. 2. Decomposition efficiency at each reaction temperature was calculated by measuring the amount of sodium chloride (chloride ion) by ion-chromatography (see Fig. 3) and the amount of remaining carbon tetrachloride by gas chromatography (see Fig. 4), respectively.


Conditions: Reagent 1: 5 M NaOH 2.0 mL/min; Sample reagent 2: CCI4 0.1 mL/min; Reaction temperature: 380, 350, 300, 250, 200, 40°C; Reaction coil 4: Hastelloy-C276 tube (0.5 mm I.D. x 5 m Length) = 981 µL; Back pressure: 30 MPa.

Conditions: Detector: Shodex CD-5; Column: Shodex IC I-524A; Shodex IC I-524AP; Eluent: 1.5 mM Phthalic acid adjusted; pH 3.0 with Tris.; Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min; Column temperature: 40°C; Injection volume: 5 µL; Sample: STD; NaCl 1.3 ppm; UNK; x 500.

Conditions: GC: GC-5890 (HP); Detector: FID 103; Column: Cemipak NOT Sus Col.6ft x 2 mm I.D.; Mobile phase: N2 at 3 kPa; Column temperature: 60°C; Injection volume: 5 µL; Sample: 5 mL/mL each of effluent at 380, 350, 300 and 40°C.
Keywords
820002S

 Download This Application
Download This Application

