FT-NIR for Rapid Identification of Illicit Drugs (Identification of MDMA in a Tablet)
June 13, 2024
Introduction
Near-Infrared (FT-NIR) diffuse reflectance (DRIFTS) spectroscopy offers some unique capabilities compared with mid-infrared (FTIR) analysis, which often requires extensive sample preparation to obtain an identifiable spectrum. As such, NIR can be useful for the non-destructive analysis of a specific sample area or provide an average of a larger sample area, depending upon the required analysis. In recent years, FT-NIR spectroscopy has been widely used for the examination of biological samples and quality control/analysis of food and medicinal products. Diffuse reflectance is ideal for this method due to the extremely straight forward sample handling that allows rapid identification of illegal drugs, such as MDMA, which can be accomplished using a spectral search data library created using NIR diffuse reflectance.

Experimental
A diffuse reflection accessory (VIR-NRF-N) is used in combination with a JASCO portable Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectrometer (VIR-9650). A sample, for example an MDMA tablet is placed directly on the sample holder, measurement is made with no additional sample preparation. An InGaAs detector is recommended to provide greater sensitivity and a rapid scanning. Principal Components Analysis (PCA) was used to simplify positive sample identification of the MDMA tablet. Where possible grouping of spectral data was confirmed based on the PCA program, and a library was created. For creating the PCA data library, 40 different sample tablets were analyzed, including 25 over-the-counter pharmaceuticals, such as gastrointestinal drugs, one type of amphetamine (AP), eight types of MDMA (street name: ecstasy), three types of methamphetamine (MA), and three types of MDA (street name: the love drug).


The utility of a simple identification system was examined by the investigation of the algorithm, the calculation parameters and a threshold established by comparing the search results from randomly selected tablets. Figure 1 shows a photograph of the diffuse reflection accessory installed in the VIR-9650. The sample tablets were placed directly on the sample holder , as shown in Figure 2. Tablets that are too small to be placed on the holder can be measured in test tube like the one shown in Figure 3.
Keywords
200-DR-0188 FT-NIR MDMA FTIR Diffuse Reflectance DRIFTS
Results
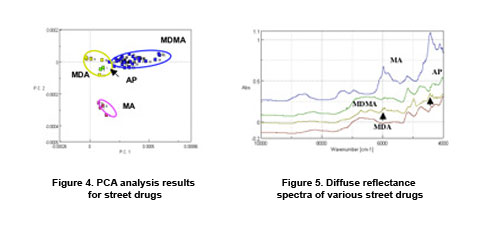
Figure 4 Shows the PCA analysis results for an MDMA tablet. Figure 5 includes examples of the Near-Infrared spectra for the four classes of illegal drugs. Sample identification can be made using the region (indicated by the arrows) where the spectral absorptions can provide specific peaks depending on the tablets’ components. The PCA method, however, provides distinct discrimination between the various drug components due to subtle variations in the NIR spectra. Since NIR spectra do not provide specific functional group peaks as are found in the mid-IR spectra, the PCA method offers better discrimination of the various drug components, strengthening the identification of the ‘unknown’ drug tablet. The FT-NIR diffuse reflection system is ideal as a rapid analysis method because the sample is simply placed on the accessor, with a measurement time of only 10 seconds. This method can become increasingly powerful for sample identification as the library data is expanded with additional standard sample data.
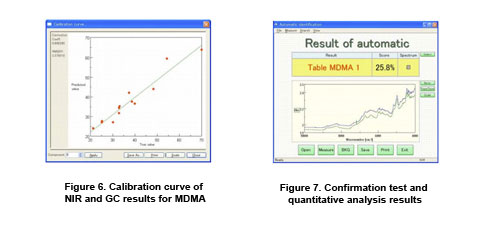
Figure 6 shows a calibration model correlating tablets containing MDMA with quantitation from GC analysis. With a correlation coefficient of R=0.966, these results demonstrate a sufficient correlation to be quantitative. This would make it possible to confirm the amount of MDMA in illicit tablets by linking identification program with the calibration model developed using GC analysis. Figure 7 is an example of the program developed for the identification of the drug formulations using PCA.
Conclusion
We have demonstrated the use of an FT-NIR analysis method utilizing PCA discrimination for the identification of various drug formulations. FT-NIR offers a rapid, non-destructive analysis method for identification of components found in various drug tablets that can be extended to provide quantitative analysis of the concentration.
Featured Products:

FT-NIR for Rapid Identification of Illicit Drugs (Identification of MDMA in a Tablet)
Introduction
Near-Infrared (FT-NIR) diffuse reflectance (DRIFTS) spectroscopy offers some unique capabilities compared with mid-infrared (FTIR) analysis, which often requires extensive sample preparation to obtain an identifiable spectrum. As such, NIR can be useful for the non-destructive analysis of a specific sample area or provide an average of a larger sample area, depending upon the required analysis. In recent years, FT-NIR spectroscopy has been widely used for the examination of biological samples and quality control/analysis of food and medicinal products. Diffuse reflectance is ideal for this method due to the extremely straight forward sample handling that allows rapid identification of illegal drugs, such as MDMA, which can be accomplished using a spectral search data library created using NIR diffuse reflectance.

Experimental
A diffuse reflection accessory (VIR-NRF-N) is used in combination with a JASCO portable Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectrometer (VIR-9650). A sample, for example an MDMA tablet is placed directly on the sample holder, measurement is made with no additional sample preparation. An InGaAs detector is recommended to provide greater sensitivity and a rapid scanning. Principal Components Analysis (PCA) was used to simplify positive sample identification of the MDMA tablet. Where possible grouping of spectral data was confirmed based on the PCA program, and a library was created. For creating the PCA data library, 40 different sample tablets were analyzed, including 25 over-the-counter pharmaceuticals, such as gastrointestinal drugs, one type of amphetamine (AP), eight types of MDMA (street name: ecstasy), three types of methamphetamine (MA), and three types of MDA (street name: the love drug).


The utility of a simple identification system was examined by the investigation of the algorithm, the calculation parameters and a threshold established by comparing the search results from randomly selected tablets. Figure 1 shows a photograph of the diffuse reflection accessory installed in the VIR-9650. The sample tablets were placed directly on the sample holder , as shown in Figure 2. Tablets that are too small to be placed on the holder can be measured in test tube like the one shown in Figure 3.
Keywords
200-DR-0188 FT-NIR MDMA FTIR Diffuse Reflectance DRIFTS
Results

Figure 4 Shows the PCA analysis results for an MDMA tablet. Figure 5 includes examples of the Near-Infrared spectra for the four classes of illegal drugs. Sample identification can be made using the region (indicated by the arrows) where the spectral absorptions can provide specific peaks depending on the tablets’ components. The PCA method, however, provides distinct discrimination between the various drug components due to subtle variations in the NIR spectra. Since NIR spectra do not provide specific functional group peaks as are found in the mid-IR spectra, the PCA method offers better discrimination of the various drug components, strengthening the identification of the ‘unknown’ drug tablet. The FT-NIR diffuse reflection system is ideal as a rapid analysis method because the sample is simply placed on the accessor, with a measurement time of only 10 seconds. This method can become increasingly powerful for sample identification as the library data is expanded with additional standard sample data.
Figure 6 shows a calibration model correlating tablets containing MDMA with quantitation from GC analysis. With a correlation coefficient of R=0.966, these results demonstrate a sufficient correlation to be quantitative. This would make it possible to confirm the amount of MDMA in illicit tablets by linking identification program with the calibration model developed using GC analysis. Figure 7 is an example of the program developed for the identification of the drug formulations using PCA.

Conclusion
We have demonstrated the use of an FT-NIR analysis method utilizing PCA discrimination for the identification of various drug formulations. FT-NIR offers a rapid, non-destructive analysis method for identification of components found in various drug tablets that can be extended to provide quantitative analysis of the concentration.

 Download This Application
Download This Application
