Measurement of Low-Molecular-Mass Heparins based on the Requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia
October 9, 2024
Introduction
Heparins are a mucopolysaccharide obtained from porcine small intestine and is widely used in the pharmaceutical field as an anticlotting drug for treatment and prevention of thromboembolism, treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, and as an anti-blood clotting agent for using extracorporeal blood circulating apparatus such as blood dialysis and artificial heart/lung.
Low-molecular-mass heparin is produced by enzymatic treatment and chemical treatment of unfractionated heparin. Low-molecular-mass heparin is classified as parnaparin, dalteparin, enoxaparin, and so on by a decomposition method and molecular weight distribution.
The European Pharmacopoeia 8th Edition (EP), molecular weight measurement method is defined in a pharmaceutical products article for low-molecular-mass heparin and the average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution are also defined in the pharmaceutical article for low-molecular-mass heparin (sodium) and low-molecular-mass heparin (calcium). SEC with a UV-Vis detector and Refractive Index detector are the defined measurement method. Using this method, a molecular weight calibration curve using low-molecular-mass heparin is created by using low-molecular-mass heparin as a reference sample. In common molecular weight measurement methods using SEC, a calibration curve is created from the retention volume and molecular weight. This common method uses oligomers and polymers with known molecular weight as the standards. However, molecular weights have to be calculated by standardizing coefficient and intensity ratio of RI and UV to create the calibration curve. This analysis is typically too complicated for normal commercial SEC software to be used.
In this application note, molecular weight measurement is made based on the European Pharmacopoeia method for the analysis of average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution using the ChromNAV Low-Molecular-Mass Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation program for ChromNAV.
Experimental
| Equipment | |
|---|---|
| Pump | PU-4185 |
| Pump Option | Degasser |
| Autosampler | AS-4050 |
| Autosampler Option | TC Unit |
| Column Oven | CO-4060 |
| Detector | UV-4075, RI-4030 |
| Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | TSKgel G2000SWXL (7.8 mm I.D. x 300 mm L, 5 µm) |
| Eluent | Aqueous solution of 0.2 M anhydrous sodium sulfate (adjusted to pH 5.0 with 0.05 M sulfuric acid) |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ML/MIN |
| Column Temp | 30°C |
| Wavelength | 234 mL |
| Injection Volume | 25 mL |
| Standard | 20 mg of low-molecular-mass heparin for calibration CRS* in 2 mL of the eluent *number average relative molecular mass: 3,800 |
| Sample | 20 mg of Parnaparin sodium CRS in 2 mL of the eluent 20 mg of Dalteparin sodium CRS in 2 mL of the eluent |
Keywords
747014H, Low-molecular-mass heparin, Parnaparin sodium, Dalteparin sodium, European Pharmacopoeia, Molecular weight measurement, UV detector, Refractive Index detector, Low-Molecular-Mass Heparin Molecular weight calculation program
Results
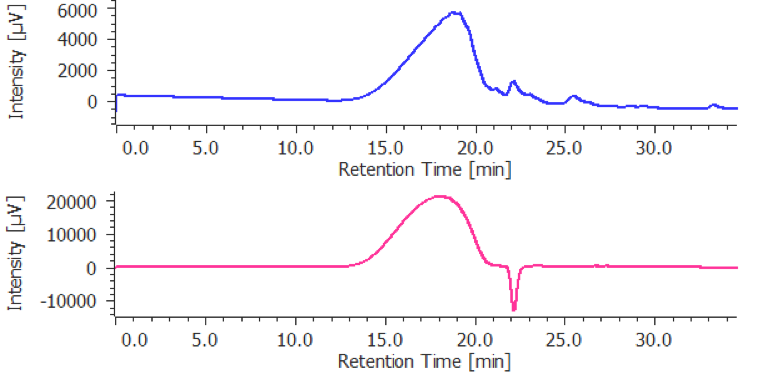
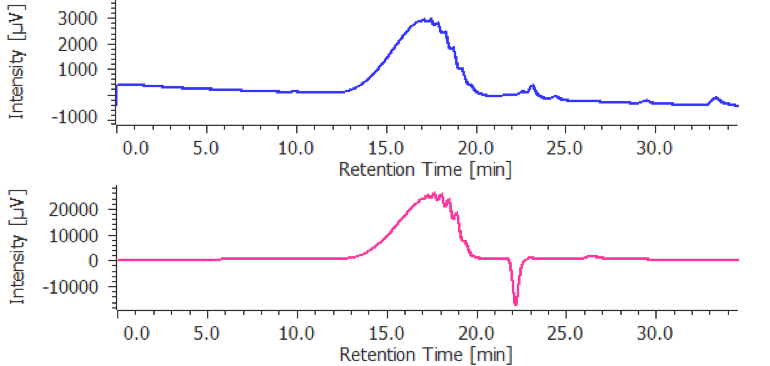
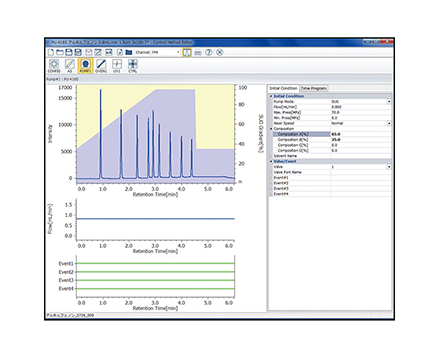
The calibration curve is created using a chromatogram of low-molecular-mass heparin for molecular weight measurement [Create Calibration Curve] displayed in the [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window. In figure 4, the calibration curve is created by using three replicate measurements of low-molecular-mass heparin for molecular weight measurement. In ChromNAV the calibration curve can be created automatically.
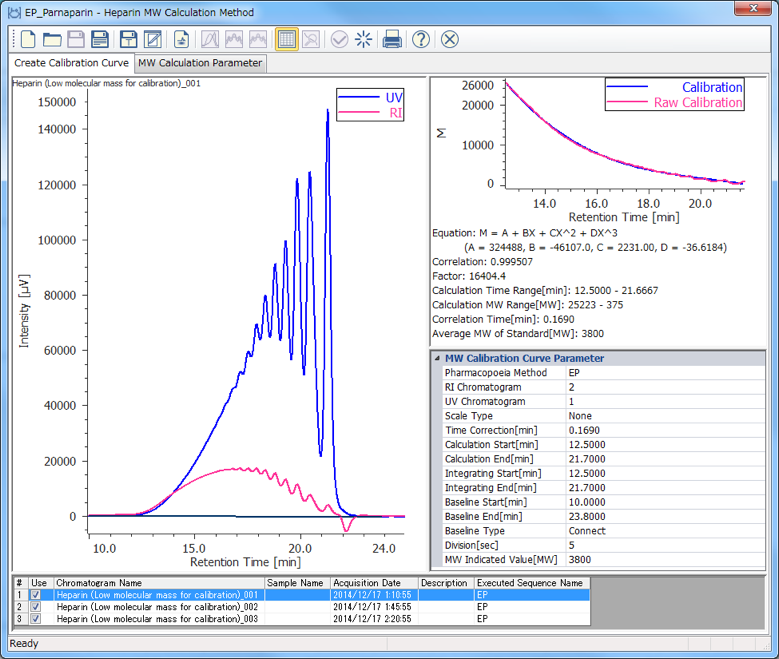
(A) chromatogram, (B) calibration curve, (C) Information about calibration curve, (D) Parameters of molecular weight calibration curve,
(E) Chromatogram list
The [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] displayed in [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window is used for setting the range for calculation of molecular weight against a sample. Figure 5 shows the [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] display of parnaparin after setting the range which is refined in the European Pharmacopoeia. The range for calculating molecular weight distribution depends on the heparin to be measured, a calibration is created for low-molecular-mass heparin (sodium), and another for dalteparin (sodium).
![APP Note 747014H fig 5 ChromNAV [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window - [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] display<br /> (A) chromatogram, (B) Calculation mode and method, (C) Range for molecular weight calculation,<br /> (D) Percentage for molecular weight range](https://jascoinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/APP-Note-747014H-fig-5.png)
(A) chromatogram, (B) Calculation mode and method, (C) Range for molecular weight calculation,
(D) Percentage for molecular weight range
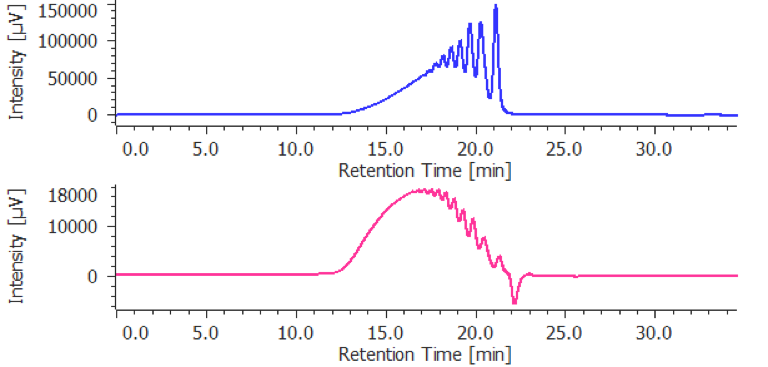
The calculation results is displayed in [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results View] by applying the prepared [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] to a sample. Figure 6 shows [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results View] for parnaparin (sodium) and dalteparin (sodium). These are created by applying prepared the [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] to their RI chromatograms. In this view, the UV chromatogram and the calibration curve can be overlaid with the RI chromatogram of the sample for determining the calculated average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution according to the European Pharmacopoeia, the calculation result table shown in figure 6 (c) is useful. In this application both the parnaparin (sodium) and dalteparin (sodium) satisfy the levels in the European Pharmacopoeia (Table 1).
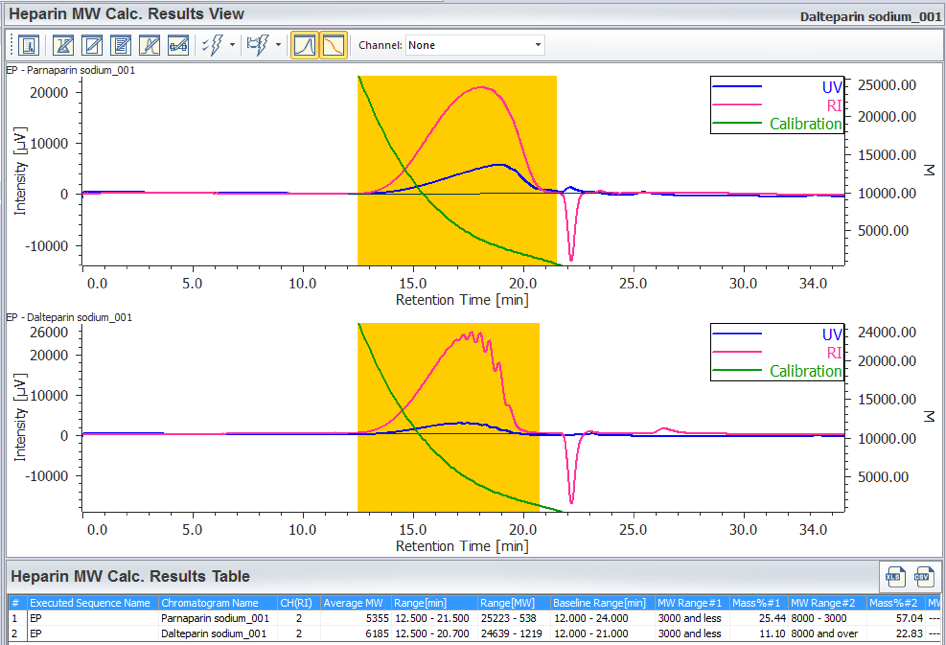
(A) Chromatogram, (B) tool buttons, (C) Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results Table
Table 1. Average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution in low-molecular-mass heparin sodium and calcium article of European Pharmacopoeia
| Low-Molecular-Mass Herapins | Range of Average Molecular Weight | Molecular Weight Distribution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M < 2000 | M < 3000 | M 2000 - 4000 | M 2000 - 8000 | M 3000 - 8000 | M > 8000 | ||
| Parnaparin Sodium | 4000 - 6000 | ≤ 30% | 50 - 60% | ||||
| Dalteparin Sodium | 5600 - 6400 | ≤ 13% | 15 - 25% | ||||
| Enoxaparin Sodium | 3800 - 5000 | 12 - 20% | 68 - 82% | ||||
| Tinzaparin Sodium | 5500 - 7500 | ≤ 10% | 60 - 72% | 22 - 36% | |||
| Nadroparin Sodium | 3600 - 5000 | ≤ 15% | 35 - 55% | 75 - 95% | |||
In this analysis, please use the pump cleaning mechanism due to a high salt concentration mobile phase.
Fresh ultrapure water is required for the cleaning mechanism before each measurement.
References
- Acupuncture, Thrombus, Hemostatic, 19 (2), 187-190 (2008).
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Heparins, low-molecular-mass monograph 0828”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Parnaparin sodium monograph 1252”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Parnaparin sodium monograph 1252”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Dalteparin sodium monograph 1195”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.1 supplement,“Enoxaparin sodium monograph 1097”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Tinzaparin sodium monograph 1271”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Nadroparin calcium monograph 1134”, (2014), Council of Europe.
Featured Products:

Measurement of Low-Molecular-Mass Heparins based on the Requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia
Introduction

Heparins are a mucopolysaccharide obtained from porcine small intestine and is widely used in the pharmaceutical field as an anticlotting drug for treatment and prevention of thromboembolism, treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, and as an anti-blood clotting agent for using extracorporeal blood circulating apparatus such as blood dialysis and artificial heart/lung.
Low-molecular-mass heparin is produced by enzymatic treatment and chemical treatment of unfractionated heparin. Low-molecular-mass heparin is classified as parnaparin, dalteparin, enoxaparin, and so on by a decomposition method and molecular weight distribution.
The European Pharmacopoeia 8th Edition (EP), molecular weight measurement method is defined in a pharmaceutical products article for low-molecular-mass heparin and the average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution are also defined in the pharmaceutical article for low-molecular-mass heparin (sodium) and low-molecular-mass heparin (calcium). SEC with a UV-Vis detector and Refractive Index detector are the defined measurement method. Using this method, a molecular weight calibration curve using low-molecular-mass heparin is created by using low-molecular-mass heparin as a reference sample. In common molecular weight measurement methods using SEC, a calibration curve is created from the retention volume and molecular weight. This common method uses oligomers and polymers with known molecular weight as the standards. However, molecular weights have to be calculated by standardizing coefficient and intensity ratio of RI and UV to create the calibration curve. This analysis is typically too complicated for normal commercial SEC software to be used.
In this application note, molecular weight measurement is made based on the European Pharmacopoeia method for the analysis of average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution using the ChromNAV Low-Molecular-Mass Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation program for ChromNAV.
Experimental
| Equipment | |
|---|---|
| Pump | PU-4185 |
| Pump Option | Degasser |
| Autosampler | AS-4050 |
| Autosampler Option | TC Unit |
| Column Oven | CO-4060 |
| Detector | UV-4075, RI-4030 |
| Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | TSKgel G2000SWXL (7.8 mm I.D. x 300 mm L, 5 µm) |
| Eluent | Aqueous solution of 0.2 M anhydrous sodium sulfate (adjusted to pH 5.0 with 0.05 M sulfuric acid) |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ML/MIN |
| Column Temp | 30°C |
| Wavelength | 234 mL |
| Injection Volume | 25 mL |
| Standard | 20 mg of low-molecular-mass heparin for calibration CRS* in 2 mL of the eluent *number average relative molecular mass: 3,800 |
| Sample | 20 mg of Parnaparin sodium CRS in 2 mL of the eluent 20 mg of Dalteparin sodium CRS in 2 mL of the eluent |

Results



The calibration curve is created using a chromatogram of low-molecular-mass heparin for molecular weight measurement [Create Calibration Curve] displayed in the [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window. In figure 4, the calibration curve is created by using three replicate measurements of low-molecular-mass heparin for molecular weight measurement. In ChromNAV the calibration curve can be created automatically.

(A) chromatogram, (B) calibration curve, (C) Information about calibration curve, (D) Parameters of molecular weight calibration curve,
(E) Chromatogram list
The [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] displayed in [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window is used for setting the range for calculation of molecular weight against a sample. Figure 5 shows the [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] display of parnaparin after setting the range which is refined in the European Pharmacopoeia. The range for calculating molecular weight distribution depends on the heparin to be measured, a calibration is created for low-molecular-mass heparin (sodium), and another for dalteparin (sodium).
![APP Note 747014H fig 5 ChromNAV [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] window - [Molecular Weight Calculation Parameter] display<br /> (A) chromatogram, (B) Calculation mode and method, (C) Range for molecular weight calculation,<br /> (D) Percentage for molecular weight range](https://jascoinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/APP-Note-747014H-fig-5.png)
(A) chromatogram, (B) Calculation mode and method, (C) Range for molecular weight calculation,
(D) Percentage for molecular weight range
The calculation results is displayed in [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results View] by applying the prepared [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] to a sample. Figure 6 shows [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results View] for parnaparin (sodium) and dalteparin (sodium). These are created by applying prepared the [Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Method] to their RI chromatograms. In this view, the UV chromatogram and the calibration curve can be overlaid with the RI chromatogram of the sample for determining the calculated average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution according to the European Pharmacopoeia, the calculation result table shown in figure 6 (c) is useful. In this application both the parnaparin (sodium) and dalteparin (sodium) satisfy the levels in the European Pharmacopoeia (Table 1).

(A) Chromatogram, (B) tool buttons, (C) Heparin Molecular Weight Calculation Results Table
Table 1. Average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution in low-molecular-mass heparin sodium and calcium article of European Pharmacopoeia
| Low-Molecular-Mass Herapins | Range of Average Molecular Weight | Molecular Weight Distribution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M < 2000 | M < 3000 | M 2000 - 4000 | M 2000 - 8000 | M 3000 - 8000 | M > 8000 | ||
| Parnaparin Sodium | 4000 - 6000 | ≤ 30% | 50 - 60% | ||||
| Dalteparin Sodium | 5600 - 6400 | ≤ 13% | 15 - 25% | ||||
| Enoxaparin Sodium | 3800 - 5000 | 12 - 20% | 68 - 82% | ||||
| Tinzaparin Sodium | 5500 - 7500 | ≤ 10% | 60 - 72% | 22 - 36% | |||
| Nadroparin Sodium | 3600 - 5000 | ≤ 15% | 35 - 55% | 75 - 95% | |||
In this analysis, please use the pump cleaning mechanism due to a high salt concentration mobile phase.
Fresh ultrapure water is required for the cleaning mechanism before each measurement.
Keywords
747014H, Low-molecular-mass heparin, Parnaparin sodium, Dalteparin sodium, European Pharmacopoeia, Molecular weight measurement, UV detector, Refractive Index detector, Low-Molecular-Mass Heparin Molecular weight calculation program
References
- Acupuncture, Thrombus, Hemostatic, 19 (2), 187-190 (2008).
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Heparins, low-molecular-mass monograph 0828”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Parnaparin sodium monograph 1252”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Parnaparin sodium monograph 1252”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Dalteparin sodium monograph 1195”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.1 supplement,“Enoxaparin sodium monograph 1097”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Tinzaparin sodium monograph 1271”, (2014), Council of Europe.
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 volume II,“Nadroparin calcium monograph 1134”, (2014), Council of Europe.

 Download This Application
Download This Application