CPL Measurement of Camphorquinone Using CPL-300 Circularly Polarized Luminescence Spectrometer
April 25, 2024
Introduction

When chiral compounds are excited with unpolarized light, the difference in emission intensities of left- and right-handed circularly polarized light can be measured. This phenomenon is called circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). While circular dichroism provides information about the ground state of chiral molecules, CPL spectroscopy probes the excited states of chiral molecules.
By combining CPL with ECD, more structural information regarding chiral molecules can be obtained. To measure sharp CPL peaks at a high resolution, the CPL spectrometer uses two prism monochromators. Both the emission and excitation monochromators are equipped with continuously variable slit drives, which allow for an appropriate wavelength and band width selection.
This application note demonstrates the measurement and analysis of camphorquinone using two complimentary techniques: circular dichroism and circularly polarized luminescence.
Experimental
18 mM of (1R)-(-) – and (1S)-(+)-camphorquinone was prepared in ethanol.
| Measurement Conditions | |||
| CD | CPL | ||
| Data Pitch | 0.1 nm | Excitation Wavelength | 440 nm |
| Scan Speed | 50 nm/min | Excitation Bandwidth | 16 nm |
| D.I.T. | 2 sec | Data Pitch | 0.1 nm |
| Bandwidth | 1 nm | Emission Bandwidth | 10 mm |
| Accumulations | 1 | Scan Speed | 50 nm/min |
| D.I.T. | 4 sec | ||
| Accumulations | 16 | ||
Keywords
260-CD-0027, Circularly Polarized Luminescence, CPL, Circular Dichroism, CD, Materials
Results
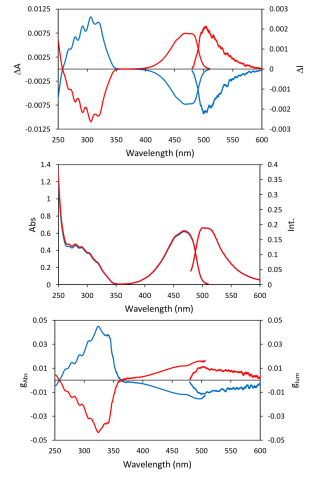
The CPL and fluorescence spectra of (1R)-(-)- and (1S)-(+)- camphorquinone were measured using a CPL-300, while CD and absorption were collected using a J-1500. The CD and CPL signals were normalized as gabs =Δ ε/ε and glum = ΔI/I, respectively. The spectra are shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion
The results are in good agreement with the camphorquinone CPL spectrum previously reported.1
References
1. Chun Ka Luk and F. S. Richardson, JACS. 1974, 96, 2006-2009.
Featured Products:

CPL Measurement of Camphorquinone Using CPL-300 Circularly Polarized Luminescence Spectrometer
Introduction

When chiral compounds are excited with unpolarized light, the difference in emission intensities of left- and right-handed circularly polarized light can be measured. This phenomenon is called circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). While circular dichroism provides information about the ground state of chiral molecules, CPL spectroscopy probes the excited states of chiral molecules.
By combining CPL with ECD, more structural information regarding chiral molecules can be obtained. To measure sharp CPL peaks at a high resolution, the CPL spectrometer uses two prism monochromators. Both the emission and excitation monochromators are equipped with continuously variable slit drives, which allow for an appropriate wavelength and band width selection.
This application note demonstrates the measurement and analysis of camphorquinone using two complimentary techniques: circular dichroism and circularly polarized luminescence.
Experimental
18 mM of (1R)-(-) – and (1S)-(+)-camphorquinone was prepared in ethanol.
| Measurement Conditions | |||
| CD | CPL | ||
| Data Pitch | 0.1 nm | Excitation Wavelength | 440 nm |
| Scan Speed | 50 nm/min | Excitation Bandwidth | 16 nm |
| D.I.T. | 2 sec | Data Pitch | 0.1 nm |
| Bandwidth | 1 nm | Emission Bandwidth | 10 mm |
| Accumulations | 1 | Scan Speed | 50 nm/min |
| D.I.T. | 4 sec | ||
| Accumulations | 16 | ||
Keywords
260-CD-0027, Circularly Polarized Luminescence, CPL, Circular Dichroism, CD, Materials
Results
The CPL and fluorescence spectra of (1R)-(-)- and (1S)-(+)- camphorquinone were measured using a CPL-300, while CD and absorption were collected using a J-1500. The CD and CPL signals were normalized as gabs =Δ ε/ε and glum = ΔI/I, respectively. The spectra are shown in Figure 1.

Conclusion
The results are in good agreement with the camphorquinone CPL spectrum previously reported.1
References
1. Chun Ka Luk and F. S. Richardson, JACS. 1974, 96, 2006-2009.

 Download This Application
Download This Application
