Simultaneous Determination of Bile Acids Utilizing an Immobilized Enzyme Column
January 5, 2024
Introduction

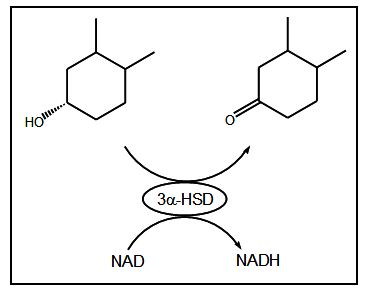
Bile acids have a common hydroxyl group located at the 3α position of their steroidal backbone. 3α-HSD (3α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase) is an enzyme that causes this hydroxyl group to be selectively oxidized in the presence of the co-enzyme NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide). In this reaction, when a molecule of bile acid is oxidized to 3-ketosteroid one NADH molecule (the reduced form of NAD) is generated and it has intense fluorescence (Ex=340 nm, Em=470 nm). In this method a standard mixture of bile acids was measured using post-column derivatization for detecting NADH generated by continuously mixing the reaction solution containing NAD with the column eluent and passing this mixed solution through a 3α-HSD enzyme-immobilized column.
Experimental
Equipment
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2089 |
| Reagent Pump: | PU-2080 |
| Column Oven: | CO-2060 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Detector: | FP-2020 |
Conditions
| Column: | Bilepak-II (4.6 mmI.D. x 125 mmL, 5 µm) |
| Enzyme Column: | Enzymepak 3?-HSD (4.0 mmI.D. x 20 mmL) |
| Eluent A: | 30 mM Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8)/Acetonitrile/Methanol (60/20/20) |
| Eluent B: | 30 mM Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8)/Acetonitrile/Methanol (40/30/30) |
| Gradient Condition: | (A/B), 0 min (100/0) 32 min (0/100) 60 min (0/100) 60.1 min (100/0) 1 cycle; 80 min |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Reagent: | 0.3 mM NAD, 1 mM EDTA-2Na, 0.05% 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM potassium dihydrogenphosphate, pH 7.8 (adjusted with potassium hydroxide) |
| Reagent Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temp.: | 25 ºC |
| Wavelength: | Ex. 345 nm, Em. 470 nm, Gain 100x |
| Injection Volume: | 10 µL |
| Standard Sample: | 15 Bile acids (50 µmol/mL each) |
Fig. 1 shows the enzyme reaction for the oxidation of bile acids and reduction of NAD
Fig. 2 shows a flow diagram for the system used to analyze the bile acids.
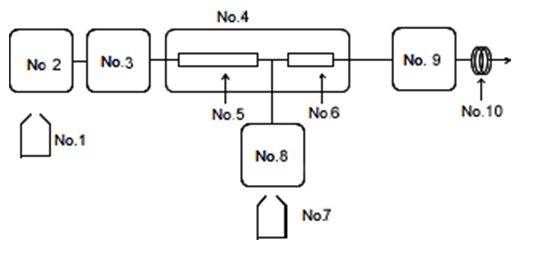
| No.1: Eluent | No.5: Column (Bilepak II) |
| No.2: PU-2089 | No.6: Enzyme column (Enzymepak 3a-HSD ) |
| No.3: Cooled Autosampler (AS-2057) | No.7: Reagent |
| No.4: Column oven (CO-2060) | No.8: Reagent pump (PU-2080) |
| No.9: Fluorescence detector (FP-2020) | |
| No.10: Backpressure coil |
Keywords
220052HRE, Bile acids, NAD, NADH, Enzymepak 3α-HSD, Bilepak-II, Fluorescence detector
Results
Fig. 3 shows the chromatogram of a standard mixture of 15 bile acids and an internal standard (I.S.), which were well separated in under 50 minutes.
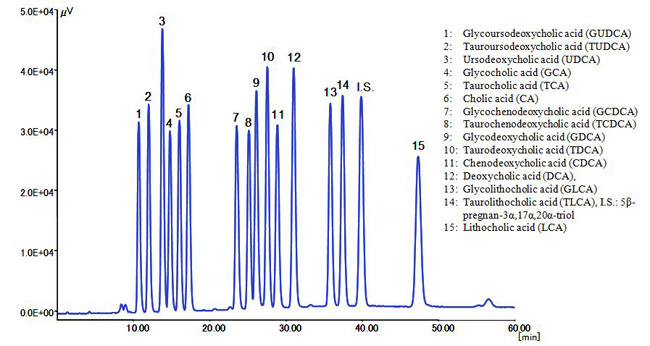
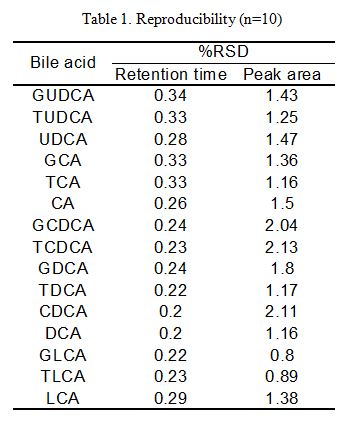
Table 1. Shows the retention time and peak area reproducibility of each bile acid when a 0.5 nmol standard mixture of bile acids (injection volume: 10 µL) (n=10). The %RSD of retention time and peak area for each component obtained was 0.2 %~ 0.34% and 0.8% ~ 2.13% respectively.
Featured Products:

Simultaneous Determination of Bile Acids Utilizing an Immobilized Enzyme Column
Introduction

Bile acids have a common hydroxyl group located at the 3α position of their steroidal backbone. 3α-HSD (3α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase) is an enzyme that causes this hydroxyl group to be selectively oxidized in the presence of the co-enzyme NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide). In this reaction, when a molecule of bile acid is oxidized to 3-ketosteroid one NADH molecule (the reduced form of NAD) is generated and it has intense fluorescence (Ex=340 nm, Em=470 nm). In this method a standard mixture of bile acids was measured using post-column derivatization for detecting NADH generated by continuously mixing the reaction solution containing NAD with the column eluent and passing this mixed solution through a 3α-HSD enzyme-immobilized column.
Experimental
Equipment
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2089 |
| Reagent Pump: | PU-2080 |
| Column Oven: | CO-2060 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Detector: | FP-2020 |
Conditions
| Column: | Bilepak-II (4.6 mmI.D. x 125 mmL, 5 µm) |
| Enzyme Column: | Enzymepak 3?-HSD (4.0 mmI.D. x 20 mmL) |
| Eluent A: | 30 mM Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8)/Acetonitrile/Methanol (60/20/20) |
| Eluent B: | 30 mM Ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8)/Acetonitrile/Methanol (40/30/30) |
| Gradient Condition: | (A/B), 0 min (100/0) 32 min (0/100) 60 min (0/100) 60.1 min (100/0) 1 cycle; 80 min |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Reagent: | 0.3 mM NAD, 1 mM EDTA-2Na, 0.05% 2-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM potassium dihydrogenphosphate, pH 7.8 (adjusted with potassium hydroxide) |
| Reagent Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temp.: | 25 ºC |
| Wavelength: | Ex. 345 nm, Em. 470 nm, Gain 100x |
| Injection Volume: | 10 µL |
| Standard Sample: | 15 Bile acids (50 µmol/mL each) |
Fig. 1 shows the enzyme reaction for the oxidation of bile acids and reduction of NAD
Fig. 2 shows a flow diagram for the system used to analyze the bile acids.


| No.1: Eluent | No.5: Column (Bilepak II) |
| No.2: PU-2089 | No.6: Enzyme column (Enzymepak 3a-HSD ) |
| No.3: Cooled Autosampler (AS-2057) | No.7: Reagent |
| No.4: Column oven (CO-2060) | No.8: Reagent pump (PU-2080) |
| No.9: Fluorescence detector (FP-2020) | |
| No.10: Backpressure coil |
Keywords
220052HRE, Bile acids, NAD, NADH, Enzymepak 3α-HSD, Bilepak-II, Fluorescence detector
Results
Fig. 3 shows the chromatogram of a standard mixture of 15 bile acids and an internal standard (I.S.), which were well separated in under 50 minutes.

Table 1. Shows the retention time and peak area reproducibility of each bile acid when a 0.5 nmol standard mixture of bile acids (injection volume: 10 µL) (n=10). The %RSD of retention time and peak area for each component obtained was 0.2 %~ 0.34% and 0.8% ~ 2.13% respectively.


 Download This Application
Download This Application