Analysis of Sugars by HPLC-ELSD
August 19, 2022
Introduction

An evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD) is a universal HPLC detector whose detection principle is based on the phenomenon of light scattering, which occurs from particles of residual non-volatile components after removing the volatile mobile phase using a combination of heat and gas nebulization. The ELSD detector uses an LED as the light source and a photomultiplier to measure change in intensity as the analyte passes through the optical path. Compounds that are typically measured using a refractive index detector or a short wavelength of a UV detector may be measured with increased sensitivity or a more stable baseline using ELSD.
In this application note, monosaccharides and disaccharides were analyzed using ELSD from a separation using a polymer NH2 column in HILIC mode.
Experimental
Instrument
| Pump | PU-2089S |
| Autosampler | AS-2057 |
| Column Oven | CO-2060 |
| Detector | ELSD-2040 |
Method
| Column | AsahiPak NH2P-50 4E (4.6 ID x 250 L mm) |
| Eluent | H2O/ACN 25:75 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temperature | 30 deg C |
| ELSD Parameters | Nebulizer temp. 30 deg C Evaporator temp. 30 deg C Gas flow rate 1.4 SLM |
| Injection Volume | 10uL |
| Standard Samples | Rhamnose, Fructose, GLucose, Sucrose, Maltose 1.0mg/mL in H2O/ACN 50:50 |
Keywords
Sugar, HILIC, Polymer NH2 column, ELSD, Rhamnose, Fructose, Glucose, Sucrose, Maltose, monosaccharides
Results
Figure 1. Chromatogram of a standard mixture of monosaccharides and disaccharides.
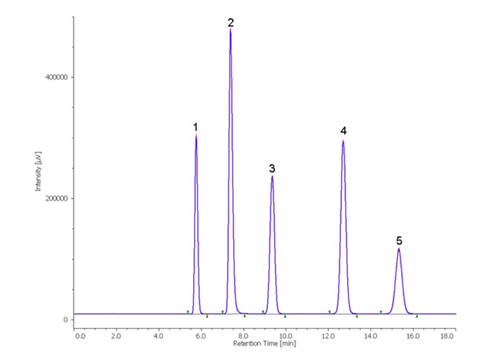
1: Rhamnose, 2: Fructose, 3: Glucose, 4: Sucrose, 5: Maltose
Featured Products:

Analysis of Sugars by HPLC-ELSD
Introduction

An evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD) is a universal HPLC detector whose detection principle is based on the phenomenon of light scattering, which occurs from particles of residual non-volatile components after removing the volatile mobile phase using a combination of heat and gas nebulization. The ELSD detector uses an LED as the light source and a photomultiplier to measure change in intensity as the analyte passes through the optical path. Compounds that are typically measured using a refractive index detector or a short wavelength of a UV detector may be measured with increased sensitivity or a more stable baseline using ELSD.
In this application note, monosaccharides and disaccharides were analyzed using ELSD from a separation using a polymer NH2 column in HILIC mode.
Experimental
Instrument
| Pump | PU-2089S |
| Autosampler | AS-2057 |
| Column Oven | CO-2060 |
| Detector | ELSD-2040 |
Method
| Column | AsahiPak NH2P-50 4E (4.6 ID x 250 L mm) |
| Eluent | H2O/ACN 25:75 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temperature | 30 deg C |
| ELSD Parameters | Nebulizer temp. 30 deg C Evaporator temp. 30 deg C Gas flow rate 1.4 SLM |
| Injection Volume | 10uL |
| Standard Samples | Rhamnose, Fructose, GLucose, Sucrose, Maltose 1.0mg/mL in H2O/ACN 50:50 |
Results
Figure 1. Chromatogram of a standard mixture of monosaccharides and disaccharides.

1: Rhamnose, 2: Fructose, 3: Glucose, 4: Sucrose, 5: Maltose
Keywords
Sugar, HILIC, Polymer NH2 column, ELSD, Rhamnose, Fructose, Glucose, Sucrose, Maltose, monosaccharides

 Download This Application
Download This Application

