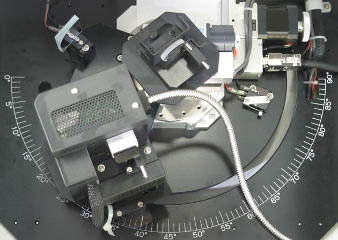
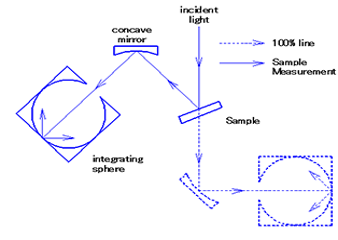
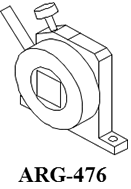
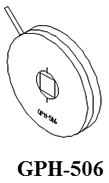
UV-Visible/NIR absolute reflectance spectroscopy can be used to evaluate the spectral properties, film thickness, angular variation or other characteristics of samples such as semiconductors, thin films and optical elements.
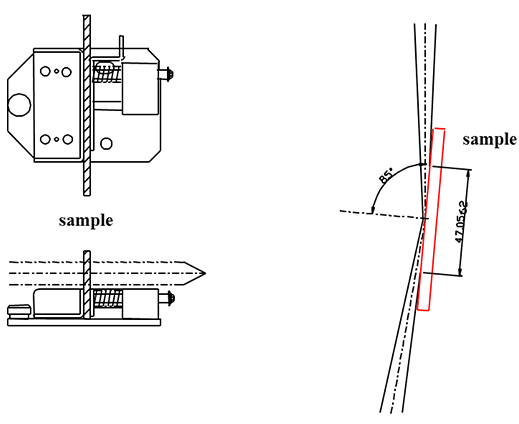
The range of absolute reflectance accessories measure specular reflecting sample (metals, semi conductors, display screens or other materials) while varying the incidence angle (all models). Several models can also be used to measure the transmittance of a sample (without diffuse transmittance). Angular dependent absolute reflectance and transmittance are measured by rotating the sample stage to select an angle of the light incident light to the sample and setting either a synchronous or asynchronous angle for the detector to measure the reflected light or transmitted light.
Diffuse reflectance can also be measured by placing the sample at the rear of the integrating sphere. Diffuse transmittance can be measured by placing the sample at the entrance of the integrating sphere.
Effect of Polarization on Absolute Reflectance
Light from a spectrophotometer that uses a grating is always polarized. The ratio of the intensities of the S and P polarized light is wavelength dependent and is also varies with the characteristics of the grating. Larger incident angles result in a greater difference in the intensity of the S and P polarized light making measurement less accurate. If absolute reflectance is measured at a large angle of incidence, a polarizer should be be set at 45° to minimize the effect of polarization differences.