Non-Ionic Surfactant Analysis by Solid-Phase Extraction
January 5, 2024
Introduction

A non-ionic surfactant contains a hydrophilic group which does not ionize when dissolved in water and has chemical properties making it unaffected by water hardness or electrolytes. A non-ionic surfactant can be used together with virtually any other type of surfactant. The use of non-ionic surfactants has increased dramatically in recent years due to the wide range of properties they offer such as ease of use, high detergency, excellent emulsification/dispersibility and low stimulation.
Water quality standards established in 2004 specify that the concentration of non-ionic surfactants must be less than 0.02 mg/L.
The established routine analysis method employs Solid-phase Extraction with Absorption Spectrophotometry where the absorbance is measured of complex formed by the reaction of the non-ionic surfactant-Co(II) with a coloring reagent 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol (PAR). In 2012, a new method based on SPE-HPLC was added to the water quality standard for the measurement of non-ionic surfactants. The water quality standard stipulates that measurement of a non-ionic surfactant should be sensitive to at least one-tenth of the acceptable concentration limits and the coefficient of variation required is better than 20%.
In this application note a non-ionic surfactant was analyzed using the newly defined SPE-HPLC method and the results are reported as below.
Experimental
Equipment
| Pump: | PU-2080 |
| Degasser: | DG-2080-53 |
| Column Oven: | CO-2065 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Detector: | UV-2070 |
Conditions
| Column: | YMC-Triart C18 (4.6 mmI.D. x 150 mmL, 5 µm) |
| Eluent: | 10 mM Sodium tetraborate/ Methanol (62/38) |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temp.: | 40 ºC |
| Wave Length: | 510 nm |
| Injection Volume: | 20 µL |
| Standard Sample: | Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether |
Keywords
840013H, SPE-HPLC, Non-ionic surfactant, Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether, 5 µm, C18 column
Results

Fig. 2 shows the chromatogram of sample with added non-ionic surfactant and table 1 shows the peak area. This result satisfies the criteria of measurement quality where the coefficient of variation of measured values is less than 20% when measuring a sample at one-tenth the acceptable concentration defined in the water quality standard.
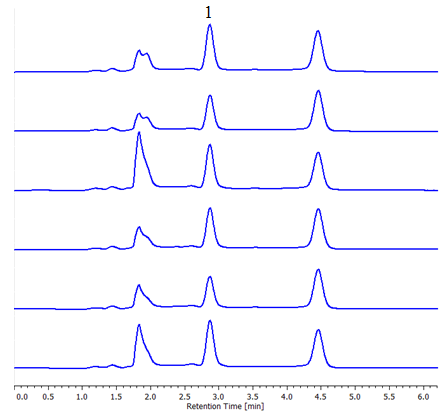
Fig. 2. Chromatogram of Sample Added with Non-ionic Surfactant* (n=6) 1: Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether (0.002 mg/L) *Sample preparation is described on Fig. 1.
Fig. 3 linearity of sample with added non-ionic surfactant. Four standard samples were measured with concentrations ranging from 0.002 to 0.01 mg/L as specified in the official analytical method, linearity was R2=0.985.
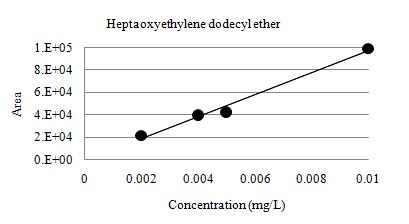
Fig. 3. Linearity of Sample with added Non-ionic Surfactant (0.002 ~ 0.01 mg/L)
Featured Products:

Non-Ionic Surfactant Analysis by Solid-Phase Extraction
Introduction

A non-ionic surfactant contains a hydrophilic group which does not ionize when dissolved in water and has chemical properties making it unaffected by water hardness or electrolytes. A non-ionic surfactant can be used together with virtually any other type of surfactant. The use of non-ionic surfactants has increased dramatically in recent years due to the wide range of properties they offer such as ease of use, high detergency, excellent emulsification/dispersibility and low stimulation.
Water quality standards established in 2004 specify that the concentration of non-ionic surfactants must be less than 0.02 mg/L.
The established routine analysis method employs Solid-phase Extraction with Absorption Spectrophotometry where the absorbance is measured of complex formed by the reaction of the non-ionic surfactant-Co(II) with a coloring reagent 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol (PAR). In 2012, a new method based on SPE-HPLC was added to the water quality standard for the measurement of non-ionic surfactants. The water quality standard stipulates that measurement of a non-ionic surfactant should be sensitive to at least one-tenth of the acceptable concentration limits and the coefficient of variation required is better than 20%.
In this application note a non-ionic surfactant was analyzed using the newly defined SPE-HPLC method and the results are reported as below.
Experimental
Equipment
| Pump: | PU-2080 |
| Degasser: | DG-2080-53 |
| Column Oven: | CO-2065 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Detector: | UV-2070 |
Conditions
| Column: | YMC-Triart C18 (4.6 mmI.D. x 150 mmL, 5 µm) |
| Eluent: | 10 mM Sodium tetraborate/ Methanol (62/38) |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column Temp.: | 40 ºC |
| Wave Length: | 510 nm |
| Injection Volume: | 20 µL |
| Standard Sample: | Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether |
Keywords
840013H, SPE-HPLC, Non-ionic surfactant, Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether, 5 µm, C18 column
Results

Fig. 2 shows the chromatogram of sample with added non-ionic surfactant and table 1 shows the peak area. This result satisfies the criteria of measurement quality where the coefficient of variation of measured values is less than 20% when measuring a sample at one-tenth the acceptable concentration defined in the water quality standard.

Fig. 2. Chromatogram of Sample Added with Non-ionic Surfactant* (n=6) 1: Heptaoxyethylene dodecyl ether (0.002 mg/L) *Sample preparation is described on Fig. 1.

Fig. 3 linearity of sample with added non-ionic surfactant. Four standard samples were measured with concentrations ranging from 0.002 to 0.01 mg/L as specified in the official analytical method, linearity was R2=0.985.

Fig. 3. Linearity of Sample with added Non-ionic Surfactant (0.002 ~ 0.01 mg/L)

 Download This Application
Download This Application