Semi-Preparative Separation of Ginsenoside in Ginseng
January 5, 2024
Introduction

Ginseng is a natural medicine derived from the araliaceae herbaceous perennial more commonly known as Asian ginseng or Korean ginseng. Ginseng has been widely reported as having many benefits including recovery from fatigue, pyretolysis, blood pressure control (low- and high- blood pressure), anti-inflammatory /antibacterial action (gastric and duodenal ulcer), hemostasis, cardiotonic action, anti-tumor action (anti-cancer action), diabetes care (blood-sugar level control and insulin secretagogue). Ginseng contains a large amount of ginsenoisides – a type of saponin. Ginsenoiside Rb1 has central depressant action and ginsenoiside Rg1 has central excitatory action, and their anti-fatigue and sedative action have been reported.
This HPLC application describes the development of a separation method for ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 using gradient elution in conventional reverse phase HPLC which can be scaled-up to semi-preparative HPLC.
Experimental
Equipment
| Conventional HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2089 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Column oven: | CO-2060 |
| Detector: | MD-2018 |
| min(50/50) -> | |
| min(80/20) |
| Semi-Preparative HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2086 (x2) |
| Mixer: | MX-2080-32 |
| (with 10 mL chamber) | |
| Autosampler: | AS-2058 |
| Column oven: | CO-2060 |
| Detector: | MD-2018 |
| min(50/50) -> | |
| min(80/20) | |
| Chromatography data system: | ChromNAV |
| Fraction collector: | ADVANTEC SCF 122SC |
| Fraction collector controller: | FC-2088-30 |
Conditions
| Conventional HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Column: | YMC-PACK Pro C18 |
| (4.6 mm ID x 250 mmL, 5 µm) | |
| Eluent: | A; Water, B; Acetonitrile, linear gradient |
| Gradient condition: | (A/B), 0 min(80/20) -> 15 |
| 20 min(50/50) -> 20.1 | |
| 1 cycle; 40 min | |
| Eluent flow rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column temp.: | 25°C |
| Wavelength: | 200 ~ 450 nm, 203 nm |
| Injection volume: | 20 µL |
| Standard sample: | Powdered Ginseng |
| (1.0g/50mL in 60% methanol) |
| Semi-Preparative HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Column: | YMC-PACK Pro C18 |
| (20 mm ID x 250 mmL, 5 µm) | |
| Eluent: | A; Water, B; Acetonitrile, linear gradient |
| Gradient condition: | (A/B), 0 min(80/20) -> 15 |
| 20 min(50/50) -> 20.1 | |
| 1 cycle; 40 min | |
| Eluent flow rate: | 15 mL/min |
| Column temp.: | 25°C |
| Wavelength: | 203 nm |
| Injection volume: | 5 mL |
| Standard sample: | Powdered Ginseng |
| (1.0g/50mL in 60% methanol) |
Preparation (extraction)
- Weigh 1.0 g of powdered ginseng and place in a centrifuge tube.
- Add 30 mL of 60% methanol and mix for 15 minutes.
- Centrifuge (3,000 rpm, 10mim) and decant the supernatant into a 50 mL measuring flask.
- Add 20 mL of 60% methanol to the residue and repeat the procedure.
- Add 60% methanol to collected supernatant in measuring flask and make up to 50 mL.
Fig. 1 Structural formulae of ginsenosides.
Keywords
742026H, Analytical HPLC, Semi-preparative HPLC, Ginseng, Asian ginseng, Ginsenoiside Rb1 and Rg1. Neutraceutical, Natural medicine
Results
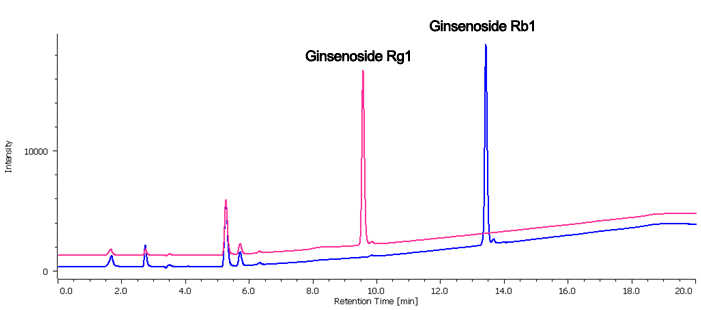
Figure 2 is Chromatogram and contour plot of extracts from ginseng powder separated using conventional HPLC. Since the retention of ginsenoiside Rg1 and Rb1 are different, the separation conditions have been determined using gradient elution. The MD-2018 PDA detector and spectral comparison was used to optimize the separation of the target compounds from other components; ginsenoisides Rg1 and Rb1 were clearly separated within 16 minutes.
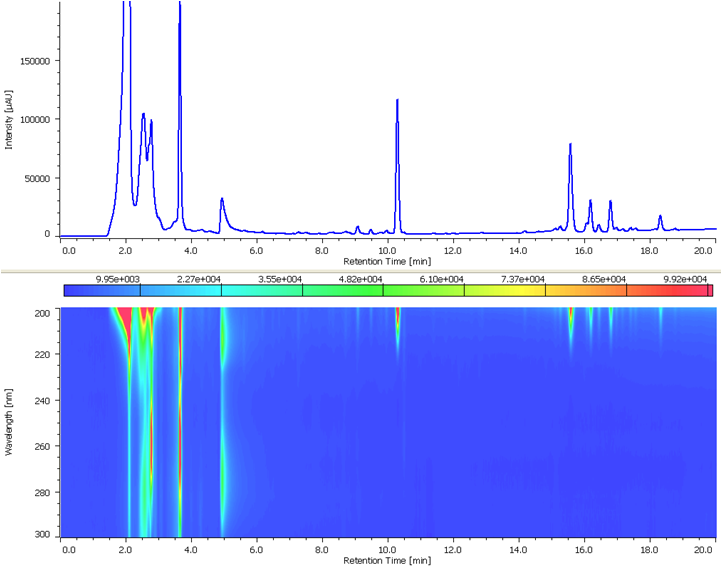
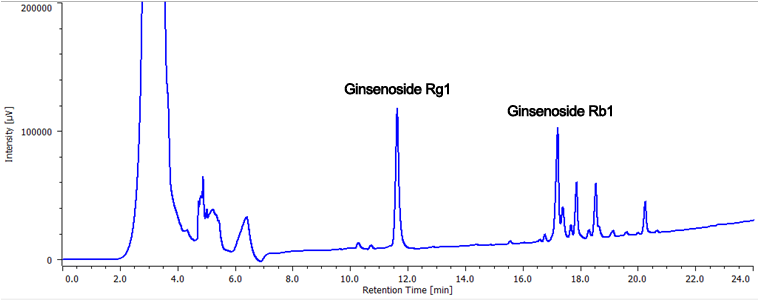
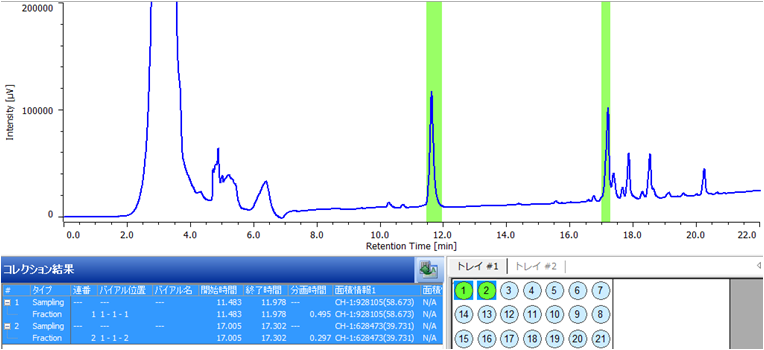
Figure 3 shows the chromatogram of the ginseng powder separated using a semi-preparative HPLC scaled-up from analytical. In order to maximize the recovery of the separated ginsenoisides a 5 mL sample volume was injected. Figure 4. shows the fraction display in the ChromNAV chromatography data system. The peaks fractions and sample rack position for the target compounds are highlighted in green. Figure 5 shows chromatograms of a purity check of the recovered fractions analyzed using the same conditions as in Figure 2. Ginsenoiside Rb1 and a minor component were not completely resolved in the semi-prep separation and small contaminant peak can be observed just after the main peak, but it was confirmed that each compound was clearly isolated.
Blank Chromatogram
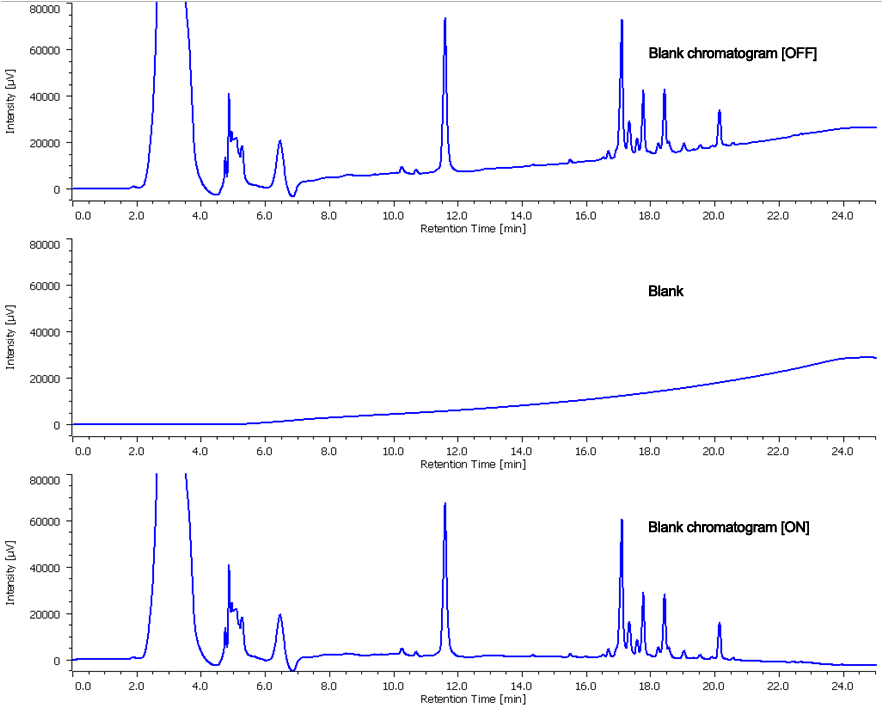
In the case of fractionation by gradient elution method, when the base line is fluctuated, it is difficult to judge the level slope correctly. For instance, the target has UV absorption only in shorter wavelength range and the eluent used for gradient elution also has UV absorption in the same range. JASCO chromatography data system ChromNAV has “blank chromatogram” function which enables to record the blank chromatogram measured in advance and show the chromatogram in which such baseline is subtracted, for judgment for fractionation. In this analysis of ginseng, since the peaks are detected at 203 nm and methanol which has UV absorption has been used in gradient, this function was employed. Figure 4 shows chromatogram with baseline fluctuation, but in practice for fractionation, the peaks were isolated under baseline corrected chromatogram.
Featured Products:

Semi-Preparative Separation of Ginsenoside in Ginseng
Introduction

Ginseng is a natural medicine derived from the araliaceae herbaceous perennial more commonly known as Asian ginseng or Korean ginseng. Ginseng has been widely reported as having many benefits including recovery from fatigue, pyretolysis, blood pressure control (low- and high- blood pressure), anti-inflammatory /antibacterial action (gastric and duodenal ulcer), hemostasis, cardiotonic action, anti-tumor action (anti-cancer action), diabetes care (blood-sugar level control and insulin secretagogue). Ginseng contains a large amount of ginsenoisides – a type of saponin. Ginsenoiside Rb1 has central depressant action and ginsenoiside Rg1 has central excitatory action, and their anti-fatigue and sedative action have been reported.
This HPLC application describes the development of a separation method for ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 using gradient elution in conventional reverse phase HPLC which can be scaled-up to semi-preparative HPLC.
Experimental
Equipment
| Conventional HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2089 |
| Autosampler: | AS-2057 |
| Column oven: | CO-2060 |
| Detector: | MD-2018 |
| min(50/50) -> | |
| min(80/20) |
| Semi-Preparative HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Eluent Pump: | PU-2086 (x2) |
| Mixer: | MX-2080-32 |
| (with 10 mL chamber) | |
| Autosampler: | AS-2058 |
| Column oven: | CO-2060 |
| Detector: | MD-2018 |
| min(50/50) -> | |
| min(80/20) | |
| Chromatography data system: | ChromNAV |
| Fraction collector: | ADVANTEC SCF 122SC |
| Fraction collector controller: | FC-2088-30 |
Conditions
| Conventional HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Column: | YMC-PACK Pro C18 |
| (4.6 mm ID x 250 mmL, 5 µm) | |
| Eluent: | A; Water, B; Acetonitrile, linear gradient |
| Gradient condition: | (A/B), 0 min(80/20) -> 15 |
| 20 min(50/50) -> 20.1 | |
| 1 cycle; 40 min | |
| Eluent flow rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Column temp.: | 25°C |
| Wavelength: | 200 ~ 450 nm, 203 nm |
| Injection volume: | 20 µL |
| Standard sample: | Powdered Ginseng |
| (1.0g/50mL in 60% methanol) |
| Semi-Preparative HPLC | |
|---|---|
| Column: | YMC-PACK Pro C18 |
| (20 mm ID x 250 mmL, 5 µm) | |
| Eluent: | A; Water, B; Acetonitrile, linear gradient |
| Gradient condition: | (A/B), 0 min(80/20) -> 15 |
| 20 min(50/50) -> 20.1 | |
| 1 cycle; 40 min | |
| Eluent flow rate: | 15 mL/min |
| Column temp.: | 25°C |
| Wavelength: | 203 nm |
| Injection volume: | 5 mL |
| Standard sample: | Powdered Ginseng |
| (1.0g/50mL in 60% methanol) |
Preparation (extraction)
- Weigh 1.0 g of powdered ginseng and place in a centrifuge tube.
- Add 30 mL of 60% methanol and mix for 15 minutes.
- Centrifuge (3,000 rpm, 10mim) and decant the supernatant into a 50 mL measuring flask.
- Add 20 mL of 60% methanol to the residue and repeat the procedure.
- Add 60% methanol to collected supernatant in measuring flask and make up to 50 mL.
Fig. 1 Structural formulae of ginsenosides.


Results
Figure 2 is Chromatogram and contour plot of extracts from ginseng powder separated using conventional HPLC. Since the retention of ginsenoiside Rg1 and Rb1 are different, the separation conditions have been determined using gradient elution. The MD-2018 PDA detector and spectral comparison was used to optimize the separation of the target compounds from other components; ginsenoisides Rg1 and Rb1 were clearly separated within 16 minutes.

Figure 3 shows the chromatogram of the ginseng powder separated using a semi-preparative HPLC scaled-up from analytical. In order to maximize the recovery of the separated ginsenoisides a 5 mL sample volume was injected. Figure 4. shows the fraction display in the ChromNAV chromatography data system. The peaks fractions and sample rack position for the target compounds are highlighted in green. Figure 5 shows chromatograms of a purity check of the recovered fractions analyzed using the same conditions as in Figure 2. Ginsenoiside Rb1 and a minor component were not completely resolved in the semi-prep separation and small contaminant peak can be observed just after the main peak, but it was confirmed that each compound was clearly isolated.



Blank Chromatogram
In the case of fractionation by gradient elution method, when the base line is fluctuated, it is difficult to judge the level slope correctly. For instance, the target has UV absorption only in shorter wavelength range and the eluent used for gradient elution also has UV absorption in the same range. JASCO chromatography data system ChromNAV has “blank chromatogram” function which enables to record the blank chromatogram measured in advance and show the chromatogram in which such baseline is subtracted, for judgment for fractionation. In this analysis of ginseng, since the peaks are detected at 203 nm and methanol which has UV absorption has been used in gradient, this function was employed. Figure 4 shows chromatogram with baseline fluctuation, but in practice for fractionation, the peaks were isolated under baseline corrected chromatogram.

Keywords
742026H, Analytical HPLC, Semi-preparative HPLC, Ginseng, Asian ginseng, Ginsenoiside Rb1 and Rg1. Neutraceutical, Natural medicine

 Download This Application
Download This Application

